DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen3-8B GRPO微调教程
话不多说,直接开始!
本文使用的测试环境为单张 A100,显存 80GB,可根据需求切换不同参数量的模型,实测4B 24G显存 is enough! 使用的框架为 Unsloth  Unsloth 是一个极其强调资源节省的框架,把所有的资源节省做到了极致,具体来讲Unsloth能够将 Llama-3、Mistral、Phi-4 和 Gemma 等大型语言模型的微调速度提升 2 倍,内存占用减少 70%,并且准确率没有任何下降! 官方文档非常全面,详细指导了如何训练自己的定制模型。其中涵盖了安装和更新 Unsloth、创建数据集、运行和部署模型等基本要素。 Unsloth 让大家在本地或在 Google Colab 和 Kaggle 等平台上训练像 Llama 3 这样的模型变得极其简单。Unsloth简化了整个训练工作流程,包括模型加载、量化、训练、评估、运行、保存、导出,以及与 Ollama、llama.cpp 和 vLLM 等推理引擎的集成。 Unsloth定期与 Hugging Face、Google 和 Meta 的团队合作,以修复 LLM 训练和模型中的错误。因此,当使用 Unsloth 进行训练或使用模型时,可以期待获得最准确的结果。 Unsloth 具有高度可定制性,允许更改聊天模板或数据集格式等内容。Unsloth还为视觉、文本转语音 (TTS)、BERT、强化学习 (RL) 等提供了预构建的脚本!此外,Unsloth支持所有训练方法和所有基于 Transformer 的模型。
Unsloth 是一个极其强调资源节省的框架,把所有的资源节省做到了极致,具体来讲Unsloth能够将 Llama-3、Mistral、Phi-4 和 Gemma 等大型语言模型的微调速度提升 2 倍,内存占用减少 70%,并且准确率没有任何下降! 官方文档非常全面,详细指导了如何训练自己的定制模型。其中涵盖了安装和更新 Unsloth、创建数据集、运行和部署模型等基本要素。 Unsloth 让大家在本地或在 Google Colab 和 Kaggle 等平台上训练像 Llama 3 这样的模型变得极其简单。Unsloth简化了整个训练工作流程,包括模型加载、量化、训练、评估、运行、保存、导出,以及与 Ollama、llama.cpp 和 vLLM 等推理引擎的集成。 Unsloth定期与 Hugging Face、Google 和 Meta 的团队合作,以修复 LLM 训练和模型中的错误。因此,当使用 Unsloth 进行训练或使用模型时,可以期待获得最准确的结果。 Unsloth 具有高度可定制性,允许更改聊天模板或数据集格式等内容。Unsloth还为视觉、文本转语音 (TTS)、BERT、强化学习 (RL) 等提供了预构建的脚本!此外,Unsloth支持所有训练方法和所有基于 Transformer 的模型。
教程概览
本教程将指导您完成 DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen3-8B 模型的 GRPO(Group Relative Policy Optimization)微调,这是一种先进的强化学习技术,专门用于提升大语言模型在特定任务上的表现。
什么是GRPO?
GRPO(Group Relative Policy Optimization)是一种强化学习优化技术,通过设计多个奖励函数来评估模型输出的不同方面,从而指导模型学习期望的行为模式。在数学推理任务中,GRPO可以帮助模型:
- 学会按照特定格式输出答案
- 提高推理过程的逻辑性
- 增强答案的准确性
- 改善输出的结构化程度
本教程的学习内容
- 环境设置: 安装Unsloth和相关依赖
- 模型加载: 加载DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen3-8B预训练模型
- LoRA配置: 设置高效的参数微调
- 数据处理: 处理GSM8K数学推理数据集
- 格式设计: 定义结构化的输出格式
- 奖励函数: 设计多维度评估体系
- GRPO训练: 执行强化学习微调
- 效果验证: 测试微调后的模型
- 模型保存: 保存训练结果
- 可视化监控: 使用SwanLab跟踪训练过程
# 安装依赖包
# pip install unsloth vllm==0.8.5.post1# 安装语言检测库
# pip install langid -qqfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModel
import torch
max_seq_length = 1024
lora_rank = 32
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = "/opt/tiger/test0/DeepSeek-R1-0528-Qwen3-8B",
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
load_in_4bit = True, # 对于LoRA 16位设置为False
fast_inference = True, # 启用vLLM快速推理
max_lora_rank = lora_rank,
gpu_memory_utilization = 0.7, # 如果内存不足请减少此值
)
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = lora_rank, # 选择任何大于0的数字!建议8, 16, 32, 64, 128
target_modules = [
"q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj",
],
lora_alpha = lora_rank*2, # *2可以加速训练
use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth", # 减少内存使用
random_state = 3407,
)GRPO对话模板
reasoning_start = None
reasoning_end = None
user_token = None
assistant_token = None
for token in tokenizer.get_added_vocab().keys():
if "think" in token and "/" in token:
reasoning_end = token
elif "think" in token:
reasoning_start = token
elif "user" in token:
user_token = token
elif "assistant" in token:
assistant_token = token
system_prompt = \
f"""你接到一个问题。
请思考这个问题并提供你的解题过程。
你必须用印尼语思考。"""
system_promptprint(tokenizer.apply_chat_template([
{"role" : "user", "content" : "What is 1+1?"},
{"role" : "assistant", "content" : f"<think>I think it's 2.2</think>2"},
{"role" : "user", "content" : "What is 1+1?"},
{"role" : "assistant", "content" : f"<think>I think it's 2.2</think>2"},
], tokenize = False, add_generation_prompt = True))数据准备
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("open-r1/DAPO-Math-17k-Processed", "en", split = "train")
dataset让我们看看第一行数据:
dataset[0]["prompt"]dataset[0]["solution"]在GSM8K中,我们注意到所有答案都有####标记,所以我们需要提取它。但对于Open R1数据集,我们可以跳过下面的处理。
def extract_hash_answer(text):
# if "####" not in text: return None
# return text.split("####")[1].strip()
return text
extract_hash_answer(dataset[0]["solution"])让我们映射数据集!并查看第一行:
dataset = dataset.map(lambda x: {
"prompt" : [
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": x["prompt"]},
],
"answer": extract_hash_answer(x["solution"]),
})
dataset[0]我们创建一个正则表达式格式来匹配推理部分和答案:
import re
# 添加可选的EOS标记匹配
solution_end_regex = rf"{reasoning_end}(.*)"
match_format = re.compile(solution_end_regex, re.DOTALL)
match_format我们验证它能正常工作:
match_format.findall(
"Let me think!</think>"\
f"Hence, the solution is 2.",
)match_format.findall(
"<think>Let me think!</think>"\
f"\n\nHence, the solution is 2",
)我们现在要创建一个奖励函数来完全匹配格式 - 如果成功匹配我们给3分:
def match_format_exactly(completions, **kwargs):
scores = []
for completion in completions:
score = 0
response = completion[0]["content"]
# 匹配是否完全符合格式!
if match_format.search(response) is not None: score += 3.0
scores.append(score)
return scores如果失败,我们希望在至少部分遵循格式时奖励模型,通过计算每个符号:
def match_format_approximately(completions, **kwargs):
scores = []
for completion in completions:
score = 0
response = completion[0]["content"]
# 计算看到多少个关键词 - 如果太多我们会惩罚!
# 如果我们看到1个,那么加一些分!
# 不需要奖励<think>因为我们总是预置它!
score += 0.5 if response.count(reasoning_start) == 1 else -1.0
score += 0.5 if response.count(reasoning_end) == 1 else -1.0
scores.append(score)
return scores我们想要提取生成的答案,并奖励或惩罚它!我们还根据答案与真实答案的比率来奖励:
def check_answer(prompts, completions, answer, **kwargs):
question = prompts[0][-1]["content"]
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
extracted_responses = [
guess.group(1)
if (guess := match_format.search(r)) is not None else None \
for r in responses
]
scores = []
for guess, true_answer in zip(extracted_responses, answer):
score = 0
if guess is None:
scores.append(-2.0)
continue
# 正确答案得5分!
if guess == true_answer:
score += 5.0
# 如果看到空格但奖励较少
elif guess.strip() == true_answer.strip():
score += 3.5
else:
# 我们也通过比率奖励接近的答案!
# 即如果答案在某个范围内,奖励它!
try:
ratio = float(guess) / float(true_answer)
if ratio >= 0.9 and ratio <= 1.1: score += 2.0
elif ratio >= 0.8 and ratio <= 1.2: score += 1.5
else: score -= 2.5 # 惩罚错误答案
except:
score -= 4.5 # 惩罚
scores.append(score)
return scores有时答案可能不是1个数字,而是像句子一样,例如"解决方案是$20" -> 我们提取20。
我们还移除可能的逗号,例如123,456
match_numbers = re.compile(
r".*?[\s]{0,}([-]?[\d\.\,]{1,})",
flags = re.MULTILINE | re.DOTALL
)
print(match_numbers.findall(" 0.34 "))
print(match_numbers.findall(" 123,456 "))
print(match_numbers.findall(" -0.234 "))
print(match_numbers.findall("17"))最后,我们将尝试强制思考过程使用印尼语。这是DeepSeek R1论文中使用的语言一致性奖励的简单版本
import langid
def get_lang(text: str) -> str:
if not text:
return "und"
lang, _ = langid.classify(text)
return lang
print(get_lang("Hello, How are you")) # 这应该返回en
print(get_lang("Aku berpikir kalau aku adalah kamu")) # 这应该返回id
print(get_lang("我在这里")) # 这应该返回zhimport re
def format_and_language_reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
scores = []
for completion_item in completions:
if not completion_item or not isinstance(completion_item[0], dict) or "content" not in completion_item[0]:
scores.append(-5.0)
print(f"警告:格式错误的完成项,分配默认低分: {completion_item}")
continue
content = completion_item[0]["content"]
lang = get_lang(content)
if lang == 'id':
score = 5.0
elif lang == 'en':
score = -3.0
elif lang == 'zh':
score = -3.0
else:
score = -5.0
scores.append(score)
return scoresprompts = [
[{"role": "assistant", "content": "What is the result of (1 + 2) * 4?"}],
[{"role": "assistant", "content": "What is the result of (3 + 1) * 2?"}],
]
completions = [
[{"role": "assistant", "content": "<think>The sum of 1 and 2 is 3, which we multiply by 4 to get 12.</think><answer>(1 + 2) * 4 = 12</answer>"}],
[{"role": "assistant", "content": "The sum of 3 and 1 is 4, which we multiply by 2 to get 8. So (3 + 1) * 2 = 8."}],
]
format_and_language_reward_func(prompts=prompts, completions=completions)我们现在准备主函数,它将打印生成的响应和真实答案,以及另一个奖励函数,通过float将文本转换为浮点数并查看是否相同。
global PRINTED_TIMES
PRINTED_TIMES = 0
global PRINT_EVERY_STEPS
PRINT_EVERY_STEPS = 5
def check_numbers(prompts, completions, answer, **kwargs):
question = prompts[0][-1]["content"]
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
extracted_responses = [
guess.group(1)
if (guess := match_numbers.search(r)) is not None else None \
for r in responses
]
scores = []
# 只在每几步打印一次
global PRINTED_TIMES
global PRINT_EVERY_STEPS
if PRINTED_TIMES % PRINT_EVERY_STEPS == 0:
print(
'*'*20 + f"问题:\n{question}", f"\n答案:\n{answer[0]}", f"\n响应:\n{responses[0]}", f"\n提取的:\n{extracted_responses[0]}"
)
PRINTED_TIMES += 1
for guess, true_answer in zip(extracted_responses, answer):
if guess is None:
scores.append(-2.5)
continue
# 转换为数字
try:
true_answer = float(true_answer.strip())
# 移除逗号,如123,456
guess = float(guess.strip().replace(",", ""))
scores.append(3.5 if guess == true_answer else -1.5)
except:
scores.append(0)
continue
return scores获取前90%的提示长度,这样我们就不会意外截断它们!
即我们将移除前10%的长提示。
tokenized = dataset.map(
lambda x: {"tokens" : tokenizer.apply_chat_template(x["prompt"], add_generation_prompt = True, tokenize = True)},
batched = True,
)
print(tokenizer.decode(tokenized[0]["tokens"]))
tokenized = tokenized.map(lambda x: {"L" : len(x["tokens"])})
import numpy as np
maximum_length = int(np.quantile(tokenized["L"], 0.9))
print("最大长度 = ", maximum_length)
# 只过滤小于90%最大长度的样本
dataset = dataset.select(np.where(np.array(tokenized["L"]) <= maximum_length)[0])
del tokenized训练模型
现在设置GRPO训练器和所有配置!
max_prompt_length = maximum_length + 1 # +1以防万一!
max_completion_length = max_seq_length - max_prompt_length
from vllm import SamplingParams
vllm_sampling_params = SamplingParams(
min_p = 0.1,
top_p = 1.0,
top_k = -1,
seed = 3407,
stop = [tokenizer.eos_token],
include_stop_str_in_output = True,
)
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
training_args = GRPOConfig(
vllm_sampling_params = vllm_sampling_params,
temperature = 1.0,
learning_rate = 5e-6,
weight_decay = 0.01,
warmup_ratio = 0.1,
lr_scheduler_type = "linear",
optim = "adamw_8bit",
logging_steps = 1,
per_device_train_batch_size = 1,
gradient_accumulation_steps = 1, # 增加到4以获得更平滑的训练
num_generations = 4, # 如果内存不足请减少
max_prompt_length = max_prompt_length,
max_completion_length = max_completion_length,
# num_train_epochs = 1, # 对于完整训练运行设置为1
max_steps = 100,
save_steps = 100,
report_to = "swanlab", # 可以使用Weights & Biases
output_dir = "outputs",
# 用于可选的训练+评估
# fp16_full_eval = True,
# per_device_eval_batch_size = 4,
# eval_accumulation_steps = 1,
# eval_strategy = "steps",
# eval_steps = 1,
)让我们运行训练器!如果你向上滚动,你会看到一个奖励表格。目标是看到reward列增加!
你可能需要等待150到200步才能看到任何效果。前100步你可能会得到0奖励。请耐心等待!
| 步骤 | 训练损失 | 奖励 | 奖励标准差 | 完成长度 | kl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.000000 | 0.125000 | 0.000000 | 200.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2 | 0.000000 | 0.072375 | 0.248112 | 200.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 3 | 0.000000 | -0.079000 | 0.163776 | 182.500000 | 0.000005 |
# 用于可选的训练+评估
# new_dataset = dataset.train_test_split(test_size = 0.01)
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
model = model,
processing_class = tokenizer,
reward_funcs = [
match_format_exactly,
match_format_approximately,
check_answer,
check_numbers,
format_and_language_reward_func,
],
args = training_args,
train_dataset = dataset,
# 用于可选的训练+评估
# train_dataset = new_dataset["train"],
# eval_dataset = new_dataset["test"],
)
trainer.train()推理
现在让我们试试刚刚训练的模型!首先,让我们先试试没有经过GRPO训练的模型:
text = "What is the sqrt of 101?"
from vllm import SamplingParams
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 1.0,
top_k = 50,
max_tokens = 1024,
)
output = model.fast_generate(
[text],
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = None,
)[0].outputs[0].text
output现在使用我们刚刚用GRPO训练的LoRA - 我们首先保存LoRA!
model.save_lora("grpo_lora")验证LoRA确实被训练了!
from safetensors import safe_open
tensors = {}
with safe_open("grpo_lora/adapter_model.safetensors", framework = "pt") as f:
# 验证A和B都非零
for key in f.keys():
tensor = f.get_tensor(key)
n_zeros = (tensor == 0).sum() / tensor.numel()
assert(n_zeros.item() != tensor.numel())现在我们加载LoRA并测试。我们在不使用自定义系统提示的情况下进行测试,这应该不会(或很少)影响模型的原始推理能力:
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Solve (x + 2)^2 = 0"},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt = True, # 生成时必须添加
tokenize = False,
)
from vllm import SamplingParams
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 1.0,
top_k = 50,
max_tokens = 2048,
)
output = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = model.load_lora("grpo_lora"),
)[0].outputs[0].text
output接下来,让我们使用系统提示进行测试,这应该使用新语言:
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": "Solve (x + 2)^2 = 0"},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt = True, # 生成时必须添加
tokenize = False,
)
from vllm import SamplingParams
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 1.0,
top_k = 50,
max_tokens = 2048,
)
output = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = model.load_lora("grpo_lora"),
)[0].outputs[0].text
output让我们比较使用系统提示但不使用LoRA的结果
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": "Solve (x + 2)^2 = 0"},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt = True, # 生成时必须添加
tokenize = False,
)
from vllm import SamplingParams
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 1.0,
top_k = 50,
max_tokens = 2048,
)
output = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = None,
)[0].outputs[0].text
output让我们取20个样本,比较使用LoRA和不使用LoRA的情况,看看哪一个有更好的正确语言使用量
sample_dataset = dataset.shuffle(seed = 3407).select(range(20))
sample_datasetwith_lora_id_count = 0
without_lora_id_count = 0
print("在20个样本上比较使用和不使用LoRA的语言使用情况:")
print("=" * 60)
for i, sample in enumerate(sample_dataset):
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": sample["prompt"][1]["content"]},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=False,
)
output_with_lora = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params=sampling_params,
lora_request=model.load_lora("grpo_lora"),
)[0].outputs[0].text
output_without_lora = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params=sampling_params,
lora_request=None,
)[0].outputs[0].text
lang_with_lora = get_lang(output_with_lora)
lang_without_lora = get_lang(output_without_lora)
if lang_with_lora == 'id':
with_lora_id_count += 1
if lang_without_lora == 'id':
without_lora_id_count += 1
# 每5个样本打印进度
if (i + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f"已处理 {i + 1}/20 个样本...")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("结果:")
print(f"使用LoRA - 印尼语响应: {with_lora_id_count}/20 ({with_lora_id_count/20*100:.1f}%)")
print(f"不使用LoRA - 印尼语响应: {without_lora_id_count}/20 ({without_lora_id_count/20*100:.1f}%)")
print(f"改进: 使用LoRA增加了{with_lora_id_count - without_lora_id_count}个印尼语响应")我们的推理模型要好得多 - 它不总是正确的,因为我们只训练了大约一个小时 - 如果我们延长序列长度并训练更长时间会更好!
保存为float16格式用于VLLM
我们还支持直接保存为float16。选择merged_16bit用于float16或merged_4bit用于int4。我们还允许lora适配器作为备选方案。使用push_to_hub_merged上传到你的Hugging Face账户!你可以去https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens获取你的个人令牌。
# 合并为16位
if False: model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_16bit",)
if False: model.push_to_hub_merged("hf/model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_16bit", token = "")
# 合并为4位
if False: model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_4bit",)
if False: model.push_to_hub_merged("hf/model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_4bit", token = "")
# 仅LoRA适配器
if False:
model.save_pretrained("model")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("model")
if False:
model.push_to_hub("hf/model", token = "")
tokenizer.push_to_hub("hf/model", token = "")GGUF / llama.cpp 转换
要保存为GGUF / llama.cpp,我们现在原生支持它!我们克隆llama.cpp并默认保存为q8_0。我们允许所有方法,如q4_k_m。使用save_pretrained_gguf进行本地保存,使用push_to_hub_gguf上传到HF。
一些支持的量化方法(完整列表在我们的Wiki页面):
q8_0- 快速转换。高资源使用,但通常可接受。q4_k_m- 推荐。对一半的attention.wv和feed_forward.w2张量使用Q6_K,其他使用Q4_K。q5_k_m- 推荐。对一半的attention.wv和feed_forward.w2张量使用Q6_K,其他使用Q5_K。
[新功能] 要微调并自动导出到Ollama,试试我们的Ollama笔记本
# 保存为8位Q8_0
if False: model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer,)
# 记住去https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens获取令牌!
# 并将hf改为你的用户名!
if False: model.push_to_hub_gguf("hf/model", tokenizer, token = "")
# 保存为16位GGUF
if False: model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "f16")
if False: model.push_to_hub_gguf("hf/model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "f16", token = "")
# 保存为q4_k_m GGUF
if False: model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "q4_k_m")
if False: model.push_to_hub_gguf("hf/model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "q4_k_m", token = "")
# 保存为多个GGUF选项 - 如果你想要多个选项会快很多!
if False:
model.push_to_hub_gguf(
"hf/model", # 将hf改为你的用户名!
tokenizer,
quantization_method = ["q4_k_m", "q8_0", "q5_k_m",],
token = "",
)本试验的试验记录
GRPO阶段
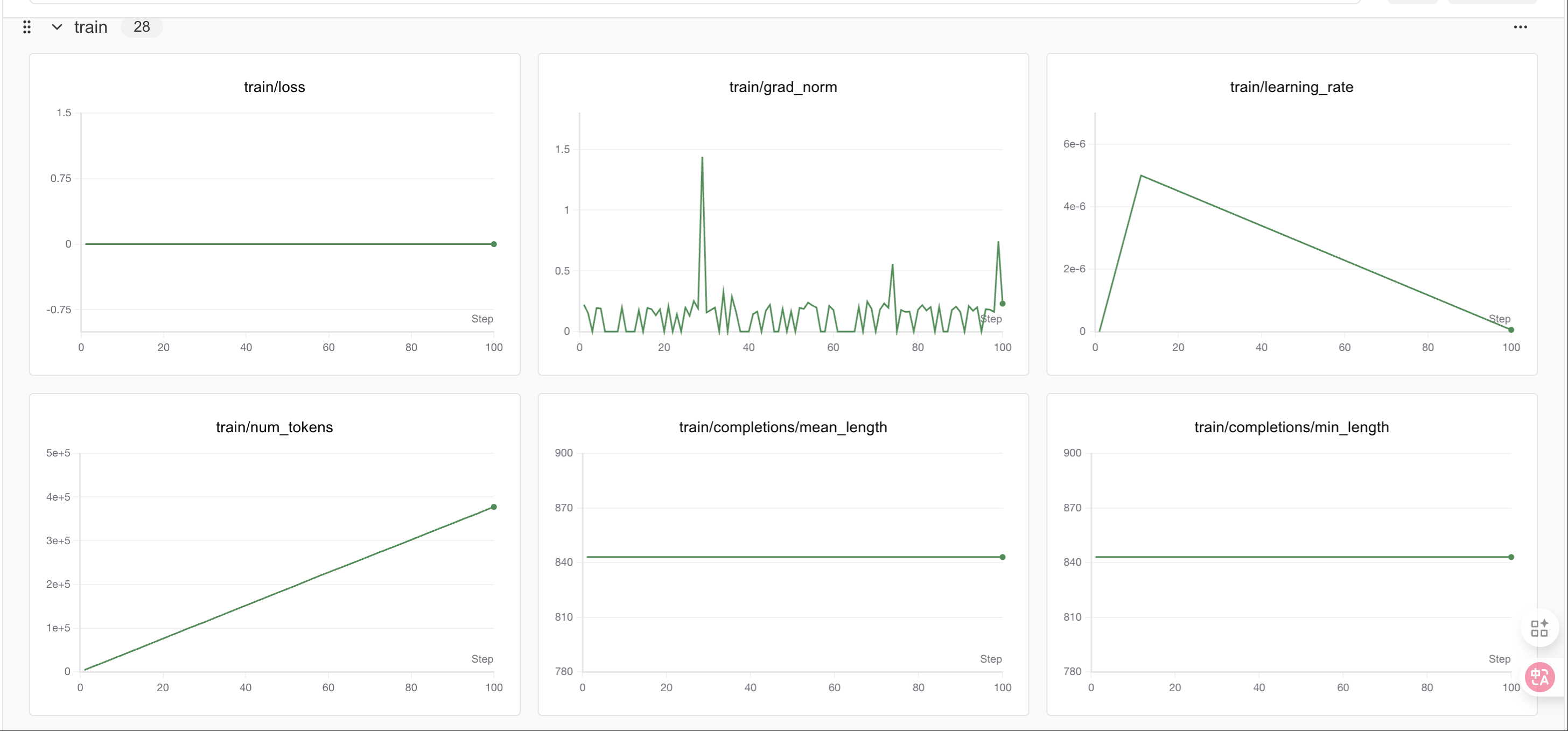 400个step之后loss会有明显变化
400个step之后loss会有明显变化
教程总结
🎉 恭喜!你已经成功完成了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen3-8B的GRPO微调教程。
本教程涵盖的核心概念:
- GRPO微调: 使用奖励函数指导模型学习特定输出格式
- LoRA技术: 高效的参数微调方法,节省显存和时间
- 奖励函数设计: 多层次评估体系,从格式到内容的全面评价
- 结构化输出: 训练模型按照特定格式输出推理过程和答案
- SwanLab监控: 实时跟踪训练进度和指标变化
学到的技能:
- ✅ 设置GRPO训练环境
- ✅ 设计多维度奖励函数
- ✅ 配置LoRA参数进行高效微调
- ✅ 处理数学推理数据集
- ✅ 监控和分析训练过程
- ✅ 保存和部署微调模型
进一步探索:
- 调整奖励函数: 设计更复杂的评估机制
- 扩展数据集: 使用更大或不同类型的数据集
- 优化参数: 尝试不同的LoRA配置和训练参数
- 模型评估: 在测试集上系统评估模型性能
- 应用部署: 将模型集成到实际应用中
注意事项:
- 本教程使用了较少的训练步数作为演示,实际应用中建议使用更多步数
- 可以根据显存情况调整批次大小和生成数量
- SwanLab提供了丰富的可视化功能,建议深入探索
感谢你的学习!如果有任何问题,欢迎查看SwanLab的实验记录或重新运行代码。
总结
Congratulations!看到了这,你已经初步实现了一个简单的RL实战,掌握了使用 Unsloth 对 Gemma3 这类大模型进行 GRPO 微调的具体操作步骤,更能体会到 Unsloth 在大幅提升训练速度、显著降低显存占用方面的强大优势,从而使在有限资源下进行复杂强化学习实验成为可能!如果支持我们的工作希望得到你的star!!这是我们持续更新的最大动力!!!
