03-GLM-4.5-Air-LoRA 及 SwanLab 可视化记录
环境配置
# 换清华镜像源
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install modelscope
pip install transformers==4.54.0
pip install accelerate
pip install datasets
pip install peft==0.16.0
pip install swanlab考虑到部分同学配置环境可能会遇到一些问题,我们在 ucloud 平台准备了 GLM-4.5-Air 的环境镜像,点击下方链接并直接创建 ucloud 示例即可。 https://www.compshare.cn/images/lUQhKDCeCdZW?referral_code=ELukJdQS3vvCwYIfgsQf2C
模型下载
from modelscope import snapshot_download
model_dir = snapshot_download('ZhipuAI/GLM-4.5-Air', cache_dir='your_model_dir', revision='master')数据集构建
对大语言模型进行 supervised-finetuning(sft,有监督微调)的数据格式如下:
{
"instruction": "回答以下用户问题,仅输出答案。",
"input": "1+1等于几?",
"output": "2"
}其中,instruction 是用户指令,告知模型其需要完成的任务;input 是用户输入,是完成用户指令所必须的输入内容;output 是模型应该给出的输出。
有监督微调的目标是让模型具备理解并遵循用户指令的能力。因此,在构建数据集时,我们应针对我们的目标任务,针对性构建数据。比如,如果我们的目标是通过大量人物的对话数据微调得到一个能够 role-play 甄嬛对话风格的模型,因此在该场景下的数据示例如下:
{
"instruction": "你父亲是谁?",
"input": "",
"output": "家父是大理寺少卿甄远道。"
}所有的示例微调数据集位于 /dataset
数据准备
LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)训练的数据是需要经过格式化、编码之后再输入给模型进行训练的,我们需要先将输入文本编码为 input_ids,将输出文本编码为 labels,编码之后的结果是向量。我们首先定义一个预处理函数,这个函数用于对每一个样本,同时编码其输入、输出文本并返回一个编码后的字典:
def process_func(example):
MAX_LENGTH = 1024 # 设置最大序列长度为1024个token
input_ids, attention_mask, labels = [], [], [] # 初始化返回值
# 适配chat_template
instruction = tokenizer(
f"[gMASK]<sop><|system|>\n现在你要扮演皇帝身边的女人--甄嬛"
f"<|user|>\n{example['instruction'] + example['input']}"
f"<|assistant|>\n<think></think>\n",
add_special_tokens=False
)
response = tokenizer(f"{example['output']}", add_special_tokens=False)
# 将instructio部分和response部分的input_ids拼接,并在末尾添加eos token作为标记结束的token
input_ids = instruction["input_ids"] + response["input_ids"]
# 注意力掩码,表示模型需要关注的位置
attention_mask = instruction["attention_mask"] + response["attention_mask"]
# 对于instruction,使用-100表示这些位置不计算loss(即模型不需要预测这部分)
labels = [-100] * len(instruction["input_ids"]) + response["input_ids"]
if len(input_ids) > MAX_LENGTH: # 超出最大序列长度截断
input_ids = input_ids[:MAX_LENGTH]
attention_mask = attention_mask[:MAX_LENGTH]
labels = labels[:MAX_LENGTH]
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"labels": labels
}GLM-4.5-Air 采用的 Chat Template格式如下:
由于 GLM-4.5-Air 是混合推理模型,因此可以手动选择开启思考模式
不开启 thinking mode
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "你好"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "你好,我是一个AI助手"},
{"role": "user", "content": "不错~"},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=False
)
print(text)[gMASK]<sop><|system|>
You are a helpful assistant.<|user|>
你好/nothink<|assistant|>
<think></think>
你好,我是一个AI助手<|user|>
不错~/nothink<|assistant|>
<think></think>开启 thinking mode
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "你好"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "你好,我是一个AI助手"},
{"role": "user", "content": "不错~"},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True
)
print(text)[gMASK]<sop><|system|>
You are a helpful assistant.<|user|>
你好<|assistant|>
<think></think>
你好,我是一个AI助手<|user|>
不错~<|assistant|>加载模型和 tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('请修改我!!!/Qwen/Qwen3-8B')
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained('请修改我!!!/Qwen/Qwen3-8B', device_map="auto", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)Lora Config
LoraConfig这个类中可以设置很多参数,比较重要的如下
task_type:模型类型,现在绝大部分decoder_only的模型都是因果语言模型CAUSAL_LMtarget_modules:需要训练的模型层的名字,主要就是attention部分的层,不同的模型对应的层的名字不同r:LoRA的秩,决定了低秩矩阵的维度,较小的r意味着更少的参数lora_alpha:缩放参数,与r一起决定了LoRA更新的强度。实际缩放比例为lora_alpha/r,在当前示例中是32 / 8 = 4倍lora_dropout:应用于LoRA层的dropout rate,用于防止过拟合
config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj", "gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"],
inference_mode=False, # 训练模式
r=8, # Lora 秩
lora_alpha=32, # Lora alpha
lora_dropout=0.1 # Dropout 比例
)Training Arguments
output_dir:模型的输出路径per_device_train_batch_size:每张卡上的batch_sizegradient_accumulation_steps: 梯度累计num_train_epochs:顾名思义epoch
args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./output/glm45_air_lora",
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
logging_steps=2,
num_train_epochs=3,
save_steps=10,
learning_rate=1e-4,
save_on_each_node=True,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
report_to="none",
)SwanLab 简介
SwanLab 是一个开源的模型训练记录工具,面向 AI 研究者,提供了训练可视化、自动日志记录、超参数记录、实验对比、多人协同等功能。在 SwanLab 上,研究者能基于直观的可视化图表发现训练问题,对比多个实验找到研究灵感,并通过在线链接的分享与基于组织的多人协同训练,打破团队沟通的壁垒。
为什么要记录训练
相较于软件开发,模型训练更像一个实验科学。一个品质优秀的模型背后,往往是成千上万次实验。研究者需要不断尝试、记录、对比,积累经验,才能找到最佳的模型结构、超参数与数据配比。在这之中,如何高效进行记录与对比,对于研究效率的提升至关重要。
实例化 SwanLabCallback
建议先在 SwanLab 官网 注册账号,然后在训练初始化阶段选择
(2) Use an existing SwanLab account 并使用 private API Key 登录
import swanlab
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallback
swanlab.login(api_key='your api key', save=True)
# 实例化SwanLabCallback
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(
project="self-llm",
experiment_name="glm45_air_lora_experiment"
)使用 Trainer 训练
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=args,
train_dataset=tokenized_id,
data_collator=DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(tokenizer=tokenizer, padding=True),
callbacks=[swanlab_callback] # 传入之前的swanlab_callback
)
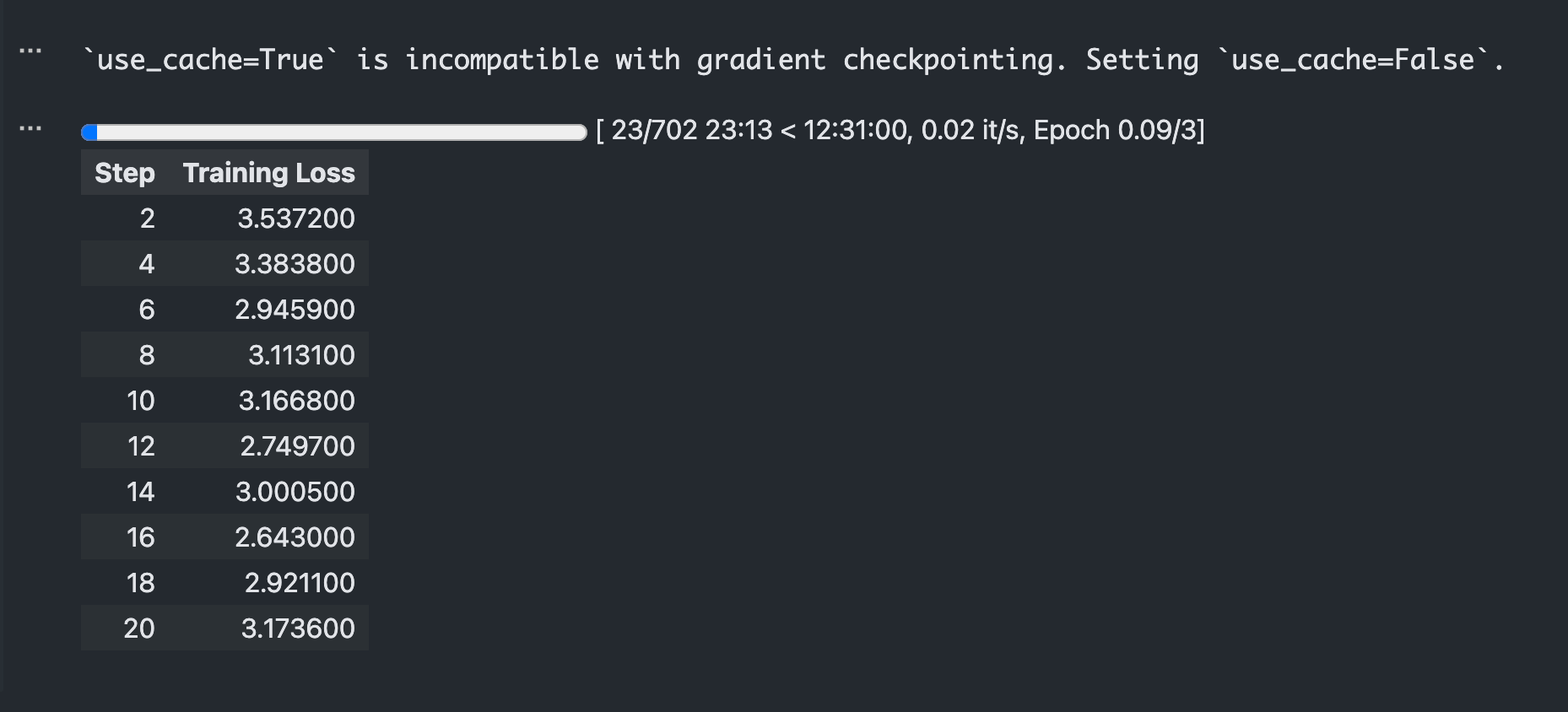
trainer.train()训练完成后,打开 SwanLab ,可以查看训练过程中记录的参数和可视化的训练 loss 曲线:
加载 lora 权重推理
得到任意 checkpoints 之后加载 lora 权重进行推理:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
from peft import PeftModel
mode_path = '/model/ModelScope/ZhipuAI/GLM-4.5-Air'
lora_path = '/workspace/output/glm45_air_lora/checkpoint-20' # 这里改称你的 lora 输出对应 checkpoint 地址
# 加载tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(mode_path)
# 加载模型
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(mode_path, device_map="auto",torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, trust_remote_code=True)
# 加载lora权重
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, model_id=lora_path)
prompt = "你是谁?"
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
[{"role": "user", "content": "假设你是皇帝身边的女人--甄嬛。"},{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True,
enable_thinking=False
)
inputs = {
"input_ids": inputs["input_ids"],
"attention_mask": inputs["attention_mask"]
}
gen_kwargs = {"max_length": 2500, "do_sample": True, "top_k": 1}
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, **gen_kwargs)
outputs = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))我是甄嬛,家父是大理寺少卿甄远道。