Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct Lora 可视化微调案例 - LaTexOCR
Qwen3-VL是截止2025年10月以来 Qwen 系列中最强的视觉语言模型。
Qwen3-VL在文本理解和生成、视觉感知和推理、扩展的上下文长度、增强的空间和视频动态理解方面都有显著改进。具有适用于从边缘到云的 Dense 和 MoE架构,并具有 Instruct 和推理增强型 Thinking 版本,可实现灵活的按需部署。
详情可以访问Qwen3-VL。
值得注意的一个增强功能是OCR能力,模型卡片中介绍到模型能支持 32 种语言(从 19 种增加);在弱光、模糊和倾斜条件下表现稳健;更适合处理稀有/古代字符和行话;改进了长文档结构解析。
本文我们将简要介绍基于 transformers、peft 等框架,使用 Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct 和 Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct 模型在 LaTeX_OCR 上进行Lora微调训练,同时使用 SwanLab 监控训练过程与评估模型效果。
备注:本教程使用的代码同时支持 2.5 系列的模型,比如 Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct 在本脚本上可以正常运行。
- 训练使用代码:在同级目录同名目录下
- 数据集:LaTeX_OCR
- 模型:Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct & Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct
- Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct 显存需求:124+GB,如果显存不足,可以将per_device_train_batch_size调小,笔者使用两张 H20 进行训练,batch size 默认是8,基于此设置,大概需要 15 分钟,批次大小对时间有影响。
- Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct 显存需求:20+GB,笔者使用 1 张 H20 进行训练,你也可以使用 24 GB显存的显卡,比如 3090,4090 等,batch size 为 1 的时候需要消耗 5 分钟。
目录
环境配置
确保你的电脑上至少有一张英伟达显卡,并已安装好了CUDA环境。本次的训练的模型如果你选择的是Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct,那么是比较大的,需要大概124GB的显存,建议用两张H20才能够完成本次实验。
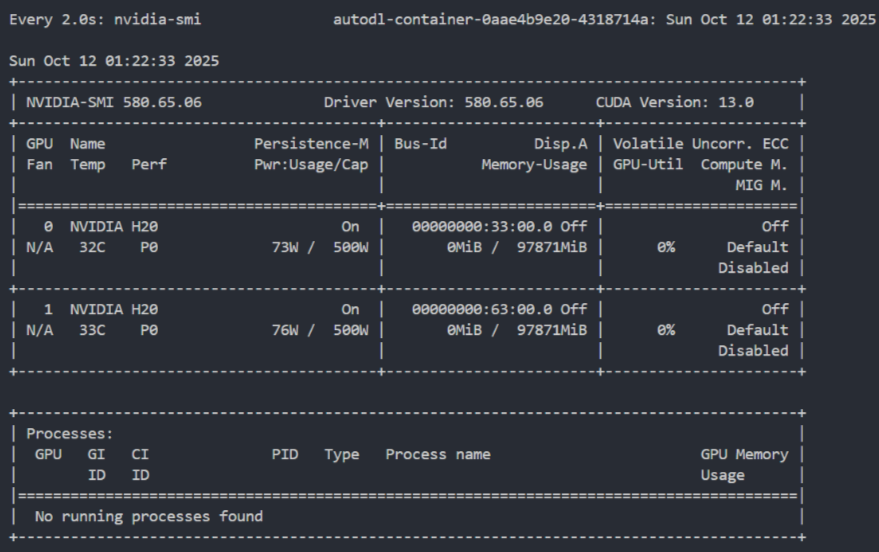
如果计算资源有限,建议使用 Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct 完成本次实验,只需要一张 24 GB 的显卡即可完成本次实验。 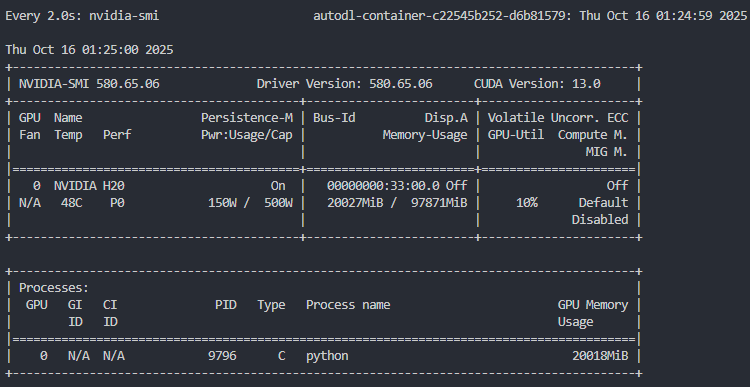
安装Python(版本>=3.12)以及能够调用CUDA加速的PyTorch,镜像采用 Pytorch2.8.0 Python3.12 CUDA12.8。
安装与Qwen3-VL微调相关的第三方库,可以使用以下命令:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip更换 pypi 源,加速库的安装
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple我们本次主要用到的一些依赖库如下:
notebook==7.4.7
numpy<2.0
datasets==4.2.0
peft==0.17.1
accelerate==1.10.1
mpmath==1.3.0
networkx==3.4.2
regex==2025.9.18
sympy==1.14.0
tokenizers==0.22.1
torch==2.8.0
torchvision>=0.23.0
transformers>=4.41.2
triton==3.4.0
qwen-vl-utils==0.0.14
matplotlib>=3.10.7
modelscope==1.30.0
python-dotenv>=1.1.1
swanlab你可以复制上面的内容,并写入到requirements.txt文件中,然后运行下面的命令安装所有依赖库:
pip install -r requirements.txt准备数据集
本次使用的数据集是linxy/LaTeX_OCR。 linxy/LaTeX_OCR是一个开源数据集,里面有五个数据集。
- small 是小数据集,样本数 110 条,用于测试。
- full 是印刷体约 100k 的完整数据集。实际上样本数略小于 100k,因为他们用 LaTeX 的抽象语法树剔除了很多不能渲染的 LaTeX。
- synthetic_handwrite 是手写体 100k 的完整数据集,基于 full 的公式,使用手写字体合成而来,可以视为人类在纸上的手写体。样本数实际上略小于 100k,理由同上。
- human_handwrite 是手写体较小数据集,更符合人类在电子屏上的手写体。主要来源于 CROHME。他们用 LaTeX 的抽象语法树校验过了。 5.human_handwrite_print 是来自 human_handwrite 的印刷体数据集,公式部分和 human_handwrite 相同,图片部分由公式用 LaTeX 渲染而来。
你可以去源数据集的页面查看数据集的子集,比如下图显示的就是数据集的各个子集字段名。 每个数据集基本都是只有两个字段,比如text和image。 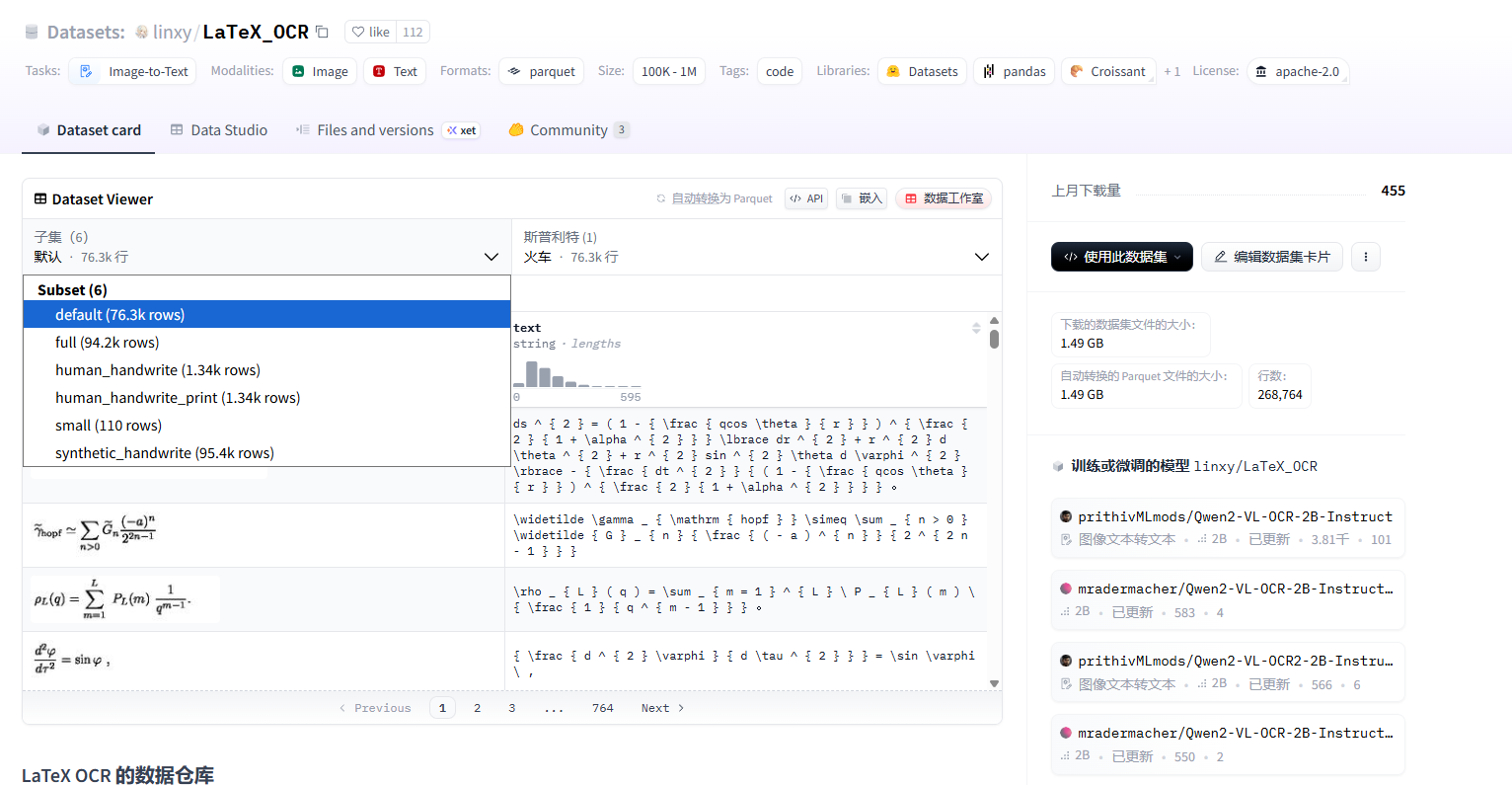
我们可以使用下面的代码进行数据集的加载。
为了便于实验,你可以在 name 中选择 small、full、synthetic_handwrite、human_handwrite 或 human_handwrite_print,并通过 split 指定 train、validation、test 等划分。
下面示例展示如何加载训练划分并快速检查样本:
from datasets import load_dataset
train_dataset = load_dataset("linxy/LaTeX_OCR", name="small", split="train")
print(train_dataset[2]["text"])
print(train_dataset[2])
print(len(train_dataset))输出:
\rho _ { L } ( q ) = \sum _ { m = 1 } ^ { L } \ P _ { L } ( m ) \ { \frac { 1 } { q ^ { m - 1 } } } .
{
'image': <PIL.PngImagePlugin.PngImageFile image mode=RGB size=200x50 at 0x15A5D6CE210>,
'text': '\\rho _ { L } ( q ) = \\sum _ { m = 1 } ^ { L } \\ P _ { L } ( m ) \\ { \\frac { 1 } { q ^ { m - 1 } } } .'
}
50若需同时获取训练、验证、测试三个划分,可直接加载整个 DatasetDict:
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("linxy/LaTeX_OCR", name="small")
print(dataset)输出:
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['image', 'text'],
num_rows: 50
})
validation: Dataset({
features: ['image', 'text'],
num_rows: 30
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['image', 'text'],
num_rows: 30
})
})模型下载
在开始模型训练之前,我们需要下载对应的模型。
为了避免由于网络问题导致的模型下载失败,我们使用modelscope对模型进行下载。
模型的地址在:
- Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct:https://modelscope.cn/models/Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct/summary
- Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct:https://modelscope.cn/models/Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct/summary
你可以使用下面的命令,将模型下载到指定的目录下面,下面是以将模型下载到 ./Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct 目录下为例:
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct --local_dir ./Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct或者是使用下面的命令,下载Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型到指定的目录下:
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct --local_dir ./Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct需要注意的是,Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct 大概需要60GB的存储空间,Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct 大概需要8GB的存储空间,在开始下载之前,如果需要微调的是 30 B的模型,确保磁盘空间闲置大小在 65 GB 以上,如果是 4 B 的模型,存储空间大小要在 10 GB 以上。
如果你需要使用我的代码在AutoDL上直接运行,那么你需要将模型下载到/root/autodl-fs/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct。
fs会长时间占用用户的空间,如果用户没有及时清理的话会一直扣费,所以我建议你换成 auto-tmp 比较好,注意,换成了 auto-tmp 之后你需要修改下加载模型的代码。
集成SwanLab
SwanLab与Transformers已经做好了集成,用法是在Trainer的callbacks参数中添加SwanLabCallback实例,就可以自动记录超参数和训练指标,简化代码如下:
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallback
from transformers import Trainer
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback()
trainer = Trainer(
...
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)首次使用SwanLab,需要先在官网注册一个账号,然后在用户设置页面复制你的API Key,然后在训练开始提示登录时粘贴即可,后续无需再次登录。
注意:SwanLab的使用是免费的,个人使用的情况下。
登录完成之后的页面是下图所示的样子。
点击其中一个,你可以看到具体的实验训练详情。
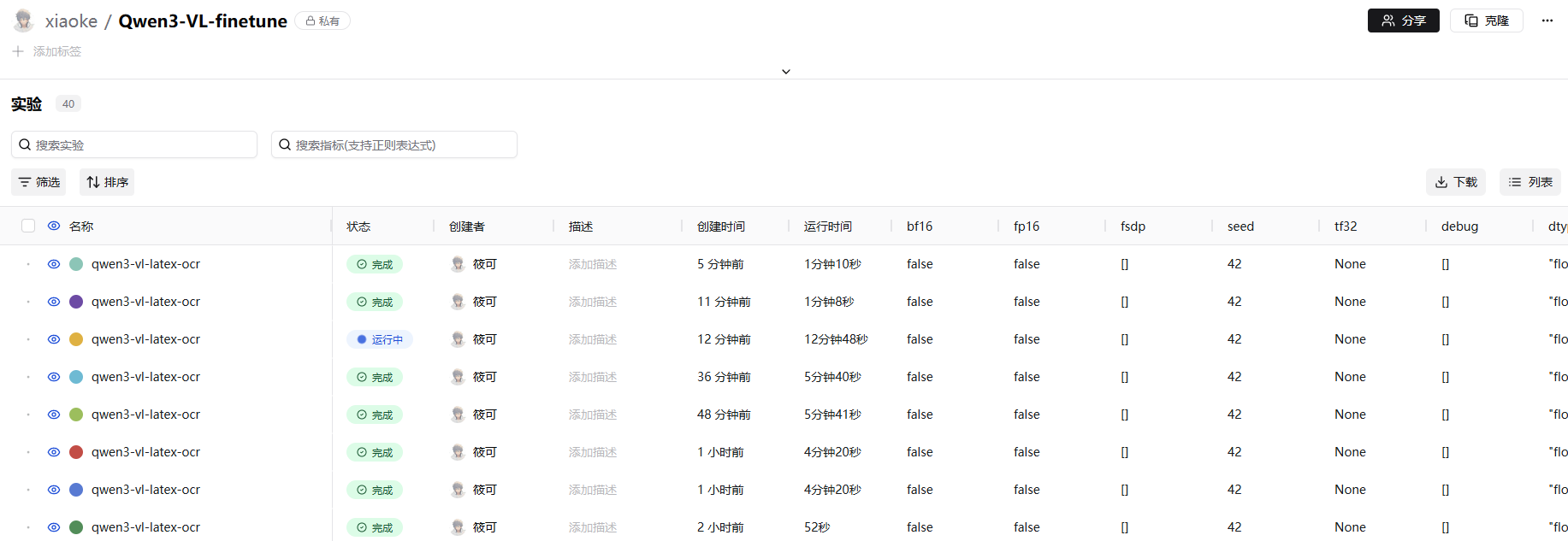
点击其中一个就会显示具体的loss变化,还有其他的一些指标。当然,SwanLab还有其他的指标可以进行监控,你可以去官网的文档中查看。
SwanLab地址:https://swanlab.cn/
在我的代码里面,api_key我设置成了从环境变量中加载,所以你需要创建一个名为.env的文件,并添加SWAN_LAB=你的API Key。
SWAN_LAB=你的API Key其中api_key可以在下面这个图中显示的位置上获取。 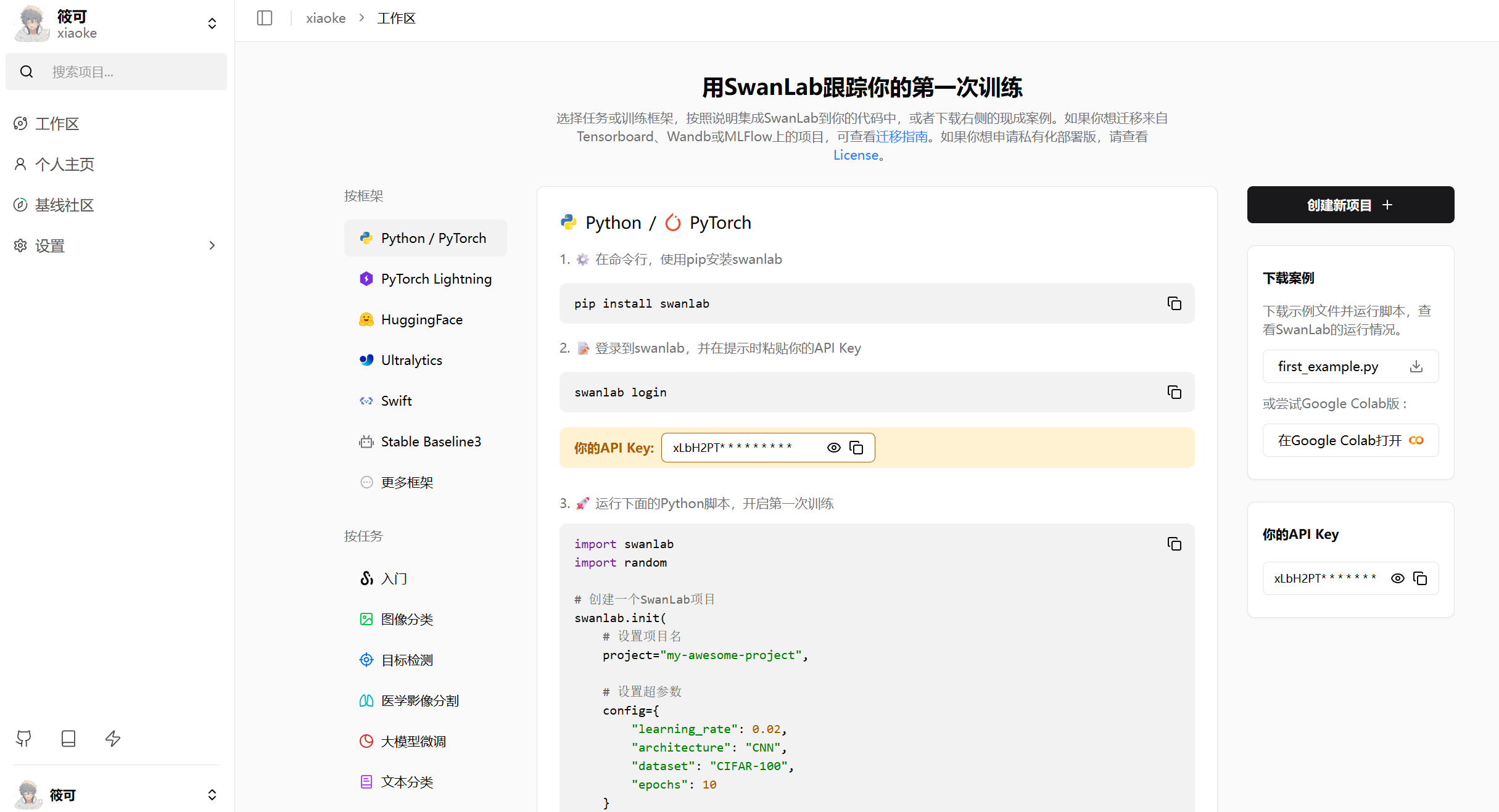
Lora 简介
Lora 的全称是 Low-Rank Adaptation,也就是低秩适配。 传统的模型微调方法,也就是全参数微调,需要更新模型中所有的参数。
Lora的核心思想是权重变化矩阵 $\Delta W$ 可以被近似地分解为两个更小的矩阵的乘积,然后仅更新两个较小的矩阵。
它在推理时不会增加额外的计算延迟。这是因为它旁路的结构可以在推理前被合并回原始的权重矩阵中。
也就是说,我们可以通过简单的矩阵加法 $W' = W_0 + BA$,将适配器的权重融合进主干网络,从而得到一个新的权重矩阵。
《LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models 》论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
Lora 配置
lora_config_dict = {
"lora_rank": 128,
"lora_alpha": 16,
"lora_dropout": 0,
}
target_modules = ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"]
config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
target_modules=target_modules,
inference_mode=False,
r=lora_config_dict["lora_rank"],
lora_alpha=lora_config_dict["lora_alpha"],
lora_dropout=lora_config_dict["lora_dropout"],
bias="none",
)上面是我们创建Lora配置的代码。如果你需要调整,可以调整lora_config_dict和target_modules,主要是设置了他们。
target_modules:LoRA 适配器要作用于模型中的哪些模块。这里设置为 ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"].
这些都是 Transformer 模型自注意力机制中的 核心线性投射层,负责生成查询、键、值和输出。
r=128: 这是 LoRA 的 秩 rank。
lora_alpha=16: 这是 LoRA 的 缩放因子 alpha,也就是公式中的α 。
lora_dropout=0: 这个参数设置了 LoRA 层的 丢弃率 dropout rate。 论文中完整的前向传播公式是下面这样的。
$$h=W_{0}x+\Delta Wx=W_{0}x+BAx$$
α 是一个常量,这样做的好处是当改变秩 r 的大小时,可以减少重新调整超参数的需要 。
带上 α 的前向传播公式是下面这样的。
$$h = W_{0}x + \frac{α}{r}BAx$$
微调的完整代码
代码
点击展开/收起微调的完整代码
import os
import torch
from typing import Any, Dict, List
from datasets import load_dataset
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
from transformers import (
TrainingArguments,
Trainer,
AutoProcessor,
AutoTokenizer,
AutoConfig,
)
import importlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallback
from dotenv import load_dotenv
class Qwen3VLDataCollator:
def __init__(self, tokenizer):
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
def __call__(self, features: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
input_id_tensors = [
torch.as_tensor(sample["input_ids"], dtype=torch.long) for sample in features
]
attention_tensors = [
torch.as_tensor(sample["attention_mask"], dtype=torch.long) for sample in features
]
label_tensors = [
torch.as_tensor(sample["labels"], dtype=torch.long) for sample in features
]
max_length = max(t.size(0) for t in input_id_tensors)
pad_id = (
self.tokenizer.pad_token_id
if getattr(self.tokenizer, "pad_token_id", None) is not None
else self.tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
if pad_id is None:
raise ValueError("pad_token_id 与 eos_token_id 均为 None,无法进行padding。")
input_ids = torch.full((len(features), max_length), pad_id, dtype=torch.long)
attention_mask = torch.zeros((len(features), max_length), dtype=torch.long)
labels = torch.full((len(features), max_length), -100, dtype=torch.long)
for idx, (ids, attn, lbl) in enumerate(zip(input_id_tensors, attention_tensors, label_tensors)):
length = ids.size(0)
input_ids[idx, :length] = ids
attention_mask[idx, :length] = attn
labels[idx, :length] = lbl
pixel_tensors = []
for sample in features:
pv = sample["pixel_values"]
if not isinstance(pv, torch.Tensor):
pv = torch.tensor(pv, dtype=torch.float32)
pixel_tensors.append(pv)
pixel_values = torch.cat(pixel_tensors, dim=0)
image_grid_thw = torch.stack(
[torch.as_tensor(sample["image_grid_thw"], dtype=torch.long).view(-1) for sample in features], dim=0
)
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"labels": labels,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"image_grid_thw": image_grid_thw,
}
PROMPT_TEXT = "Transcribe the LaTeX of this image."
def process_func(example, tokenizer, processor):
MAX_LENGTH = 8192
image = example["image"]
output_content = example["text"]
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": image,
},
{"type": "text", "text": PROMPT_TEXT},
],
}
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True
)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
do_resize=True,
)
instruction_input_ids = inputs["input_ids"][0]
instruction_attention_mask = inputs["attention_mask"][0]
instruction_pixel_values = inputs["pixel_values"]
instruction_image_grid_thw = inputs["image_grid_thw"][0]
response = tokenizer(f"{output_content}", add_special_tokens=False)
response_input_ids = response["input_ids"]
response_attention_mask = response.get(
"attention_mask", [1] * len(response_input_ids)
)
eos_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
if eos_token_id is not None:
if not response_input_ids or response_input_ids[-1] != eos_token_id:
response_input_ids = response_input_ids + [eos_token_id]
response_attention_mask = response_attention_mask + [1]
else:
pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
if pad_token_id is None:
raise ValueError("需要定义 eos_token_id 或 pad_token_id 才能结束响应序列。")
response_input_ids = response_input_ids + [pad_token_id]
response_attention_mask = response_attention_mask + [1]
input_ids = instruction_input_ids + response_input_ids
attention_mask = instruction_attention_mask + response_attention_mask
labels = (
[-100] * len(instruction_input_ids) + response_input_ids
)
if len(input_ids) > MAX_LENGTH:
input_ids = input_ids[:MAX_LENGTH]
attention_mask = attention_mask[:MAX_LENGTH]
labels = labels[:MAX_LENGTH]
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"labels": labels,
"pixel_values": instruction_pixel_values,
"image_grid_thw": instruction_image_grid_thw,
}
def main():
load_dotenv()
os.environ["SWANLAB_API_KEY"] = os.getenv("SWAN_LAB")
data_fraction = 0.002
ds = load_dataset("linxy/LaTeX_OCR", "synthetic_handwrite")
ds = ds.shuffle(seed=222)
train_data = ds["train"].select(range(int(len(ds["train"]) * data_fraction)))
print(f"训练数据大小: {len(train_data)}")
test_data = ds["test"].select(range(int(len(ds["test"]) * data_fraction)))
print(f"测试数据大小: {len(test_data)}")
# model_id = "/root/autodl-fs/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# model_id = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct"
# output_dir = "/root/autodl-fs/output/Qwen3-VL-30B"
model_id = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
output_dir = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False, trust_remote_code=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False)
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), trust_remote_code=True)
arch = (config.architectures or [None])[0]
module_name = f"transformers.models.{config.model_type}.modeling_{config.model_type}"
module = importlib.import_module(module_name)
model_cls = getattr(module, arch)
model = model_cls.from_pretrained(
model_id,
cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"),
device_map="auto",
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model.to(dtype=torch.bfloat16)
model.config.use_cache = False
map_kwargs = {"tokenizer": tokenizer, "processor": processor}
train_dataset = train_data.map(
process_func,
remove_columns=train_data.column_names,
fn_kwargs=map_kwargs,
)
lora_config_dict = {
"lora_rank": 128,
"lora_alpha": 16,
"lora_dropout": 0,
}
target_modules = ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"]
config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
target_modules=target_modules,
inference_mode=False,
r=lora_config_dict["lora_rank"],
lora_alpha=lora_config_dict["lora_alpha"],
lora_dropout=lora_config_dict["lora_dropout"],
bias="none",
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
peft_model.enable_input_require_grads()
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(
project="Qwen3-VL-finetune",
experiment_name="qwen3-vl-latex-ocr",
config={
"model": model_id,
"dataset": "linxy/LaTeX_OCR",
"prompt": PROMPT_TEXT,
"train_data_number": len(train_data),
"lora_rank": lora_config_dict["lora_rank"],
"lora_alpha": lora_config_dict["lora_alpha"],
"lora_dropout": lora_config_dict["lora_dropout"],
},
)
args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=output_dir,
per_device_train_batch_size=8, # 每个GPU的batch size
gradient_accumulation_steps=1, # 梯度累积步数
logging_steps=10,
logging_first_step=5,
num_train_epochs=8, # 训练轮数
save_steps=50, # 每多少步保存一次模型
save_total_limit=3, # 最多保存模型数量
learning_rate=1e-4, # 学习率
gradient_checkpointing=True, # 梯度检查点
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs={"use_reentrant": False},
report_to="none",
)
eval_dataset = test_data.map(
process_func,
remove_columns=test_data.column_names,
fn_kwargs=map_kwargs,
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=peft_model,
args=args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
data_collator=Qwen3VLDataCollator(tokenizer=tokenizer),
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)
trainer.train()
logs = trainer.state.log_history
steps = [log['step'] for log in logs if 'loss' in log]
losses = [log['loss'] for log in logs if 'loss' in log]
plt.plot(steps, losses)
plt.xlabel('Step')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss (Qwen3-VL-30B)')
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output_dir, "training_loss.png"))
trainer.model.save_pretrained(output_dir)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(output_dir)
processor.save_pretrained(output_dir)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()训练配置
训练配置如下:
args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=output_dir,
per_device_train_batch_size=8, # 每个GPU的batch size
gradient_accumulation_steps=1, # 梯度累积步数
logging_steps=10,
logging_first_step=5,
num_train_epochs=8, # 训练轮数
save_steps=50, # 每多少步保存一次模型
save_total_limit=3, # 最多保存模型数量
learning_rate=1e-4, # 学习率
gradient_checkpointing=True, # 梯度检查点
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs={"use_reentrant": False},
report_to="none",
)模型路径设置
模型路径设置的部分是:
# model_id = "/root/autodl-fs/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# model_id = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct"
# output_dir = "/root/autodl-fs/output/Qwen3-VL-30B"
model_id = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
output_dir = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B"你可以基于我原有的代码进行修改,可以替换成你想要进行微调的模型。
对比微调前后模型的输出结果
代码
我们可以使用下面的代码来对比微调前后模型的输出结果。
点击查看代码
import os
import sys
from typing import List, Tuple
import torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from peft import PeftModel
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoTokenizer, AutoConfig
import importlib
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
PROMPT_TEXT = "Transcribe the LaTeX of this image."
# 使用本地基础模型与LoRA目录
# BASE_MODEL_ID = "/root/autodl-fs/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# PEFT_DIR = "/root/autodl-fs/output/Qwen3-VL-30B"
BASE_MODEL_ID = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
PEFT_DIR = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B"
# 是否在内存内合并LoRA(不落盘)
MERGE_LORA_IN_MEMORY = True
NUM_TEST_SAMPLES = 5
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
DTYPE = torch.bfloat16 if DEVICE.type == "cuda" else torch.float32
def load_backbone(model_id: str):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False, trust_remote_code=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False, trust_remote_code=True)
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_id, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), trust_remote_code=True)
arch = (config.architectures or [None])[0]
module_name = f"transformers.models.{config.model_type}.modeling_{config.model_type}"
module = importlib.import_module(module_name)
model_cls = getattr(module, arch)
model = model_cls.from_pretrained(
model_id,
cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"),
device_map="auto" if DEVICE.type == "cuda" else None,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model.to(dtype=DTYPE)
return model, tokenizer, processor
def load_lora_model(peft_dir: str, base_model_id: str = BASE_MODEL_ID):
if not os.path.isdir(peft_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"未找到微调模型目录: {peft_dir}")
# 基座
base_model, _base_tok, _base_proc = load_backbone(base_model_id)
# 先加载LoRA
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_dir)
model = peft_model
if MERGE_LORA_IN_MEMORY:
try:
model = peft_model.merge_and_unload()
print("LoRA内存合并成功。")
except Exception:
print("警告: LoRA内存合并失败,继续使用未合并模型。")
# 合并失败则退回未合并模型
model = peft_model
model.to(dtype=DTYPE)
model.eval()
# tokenizer/processor 优先从LoRA目录读取,保证chat_template与词表一致
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(peft_dir, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False, trust_remote_code=True)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(peft_dir, cache_dir=os.environ.get("HF_HOME", "./"), use_fast=False, trust_remote_code=True)
return model, tokenizer, processor
def build_inputs(processor, image, prompt_text: str):
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt_text},
],
}
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(text=[text], images=image_inputs, videos=video_inputs, do_resize=True)
return inputs
def ensure_block_dollars(text: str) -> str:
if text is None:
return "$$$$"
s = str(text).strip()
if s.startswith("$$") and s.endswith("$$"):
return s
if s.startswith("$") and s.endswith("$") and not s.startswith("$$") and not s.endswith("$$"):
inner = s[1:-1].strip()
return f"$${inner}$$"
if s.count("$$") >= 2:
return s
return f"$${s}$$"
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate_answer(model, tokenizer, processor, image, max_new_tokens: int = 512) -> str:
inputs = build_inputs(processor, image, PROMPT_TEXT)
input_ids = torch.as_tensor(inputs["input_ids"], device=DEVICE)
if input_ids.ndim == 1:
input_ids = input_ids.unsqueeze(0)
attention_mask = inputs.get("attention_mask", None)
if attention_mask is not None:
attention_mask = torch.as_tensor(attention_mask, device=DEVICE)
if attention_mask.ndim == 1:
attention_mask = attention_mask.unsqueeze(0)
pixel_values = inputs.get("pixel_values")
pixel_values = torch.as_tensor(pixel_values, device=DEVICE)
image_grid_thw = inputs.get("image_grid_thw")
image_grid_thw = torch.as_tensor(image_grid_thw, device=DEVICE)
gen_kwargs = {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"pixel_values": pixel_values,
"max_new_tokens": max_new_tokens,
"do_sample": False,
"use_cache": True,
}
if attention_mask is not None:
gen_kwargs["attention_mask"] = attention_mask
if image_grid_thw is not None:
gen_kwargs["image_grid_thw"] = image_grid_thw
outputs = model.generate(**gen_kwargs)
gen_seq = outputs[0].tolist()
prompt_len = input_ids.shape[1]
gen_ids = gen_seq[prompt_len:]
text = tokenizer.decode(gen_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
return text.strip()
def main():
print("Loading dataset linxy/LaTeX_OCR (synthetic_handwrite)...")
ds = load_dataset("linxy/LaTeX_OCR", "synthetic_handwrite")
ds = ds.shuffle(seed=222)
# test_split = ds["train"].select(range(NUM_TEST_SAMPLES))
test_split = ds["test"].select(range(NUM_TEST_SAMPLES))
print("Loading base model...")
base_model, base_tokenizer, base_processor = load_backbone(BASE_MODEL_ID)
try:
if hasattr(base_model, "gradient_checkpointing"):
base_model.gradient_checkpointing_disable()
if hasattr(base_model, "config"):
base_model.config.use_cache = True
if hasattr(base_model, "generation_config") and base_model.generation_config is not None:
base_model.generation_config.use_cache = True
except Exception:
pass
base_model.eval()
print(f"Loading LoRA fine-tuned model from: {PEFT_DIR}")
try:
lora_model, lora_tokenizer, lora_processor = load_lora_model(PEFT_DIR, BASE_MODEL_ID)
try:
if hasattr(lora_model, "gradient_checkpointing"):
lora_model.gradient_checkpointing_disable()
if hasattr(lora_model, "config"):
lora_model.config.use_cache = True
except Exception:
pass
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载微调模型失败: {e}")
print("仅对基础模型进行推理对比。")
lora_model = None
lora_tokenizer = base_tokenizer
lora_processor = base_processor
print(f"\n===== Inference Comparison on {NUM_TEST_SAMPLES} samples =====\n")
for idx, sample in enumerate(test_split):
image = sample["image"]
gt = sample.get("text", "")
print(f"[Sample {idx}]------------------------------")
print(f"GT: {ensure_block_dollars(gt)}")
base_pred = ensure_block_dollars(generate_answer(base_model, base_tokenizer, base_processor, image))
print(f"Base: {base_pred}")
if lora_model is not None:
lora_pred = ensure_block_dollars(generate_answer(lora_model, lora_tokenizer, lora_processor, image))
print(f"LoRA: {lora_pred}")
else:
print("LoRA: <not loaded>")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()运行配置
模型路径设置的位置和其他的一些设置项,在文件的开始部分代码中,具体如下。
PROMPT_TEXT = "Transcribe the LaTeX of this image." # 使用的提示词。
# 使用本地基础模型与LoRA目录
# BASE_MODEL_ID = "/root/autodl-fs/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct"
# PEFT_DIR = "/root/autodl-fs/output/Qwen3-VL-30B"
BASE_MODEL_ID = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
PEFT_DIR = "/root/autodl-tmp/Qwen3-VL-4B"
# 是否在内存内合并LoRA(不落盘)
MERGE_LORA_IN_MEMORY = True
NUM_TEST_SAMPLES = 5 # 是使用的测试样本数模型微调效果
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct
下面的图是Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct模型微调图表,使用的batch size为8。
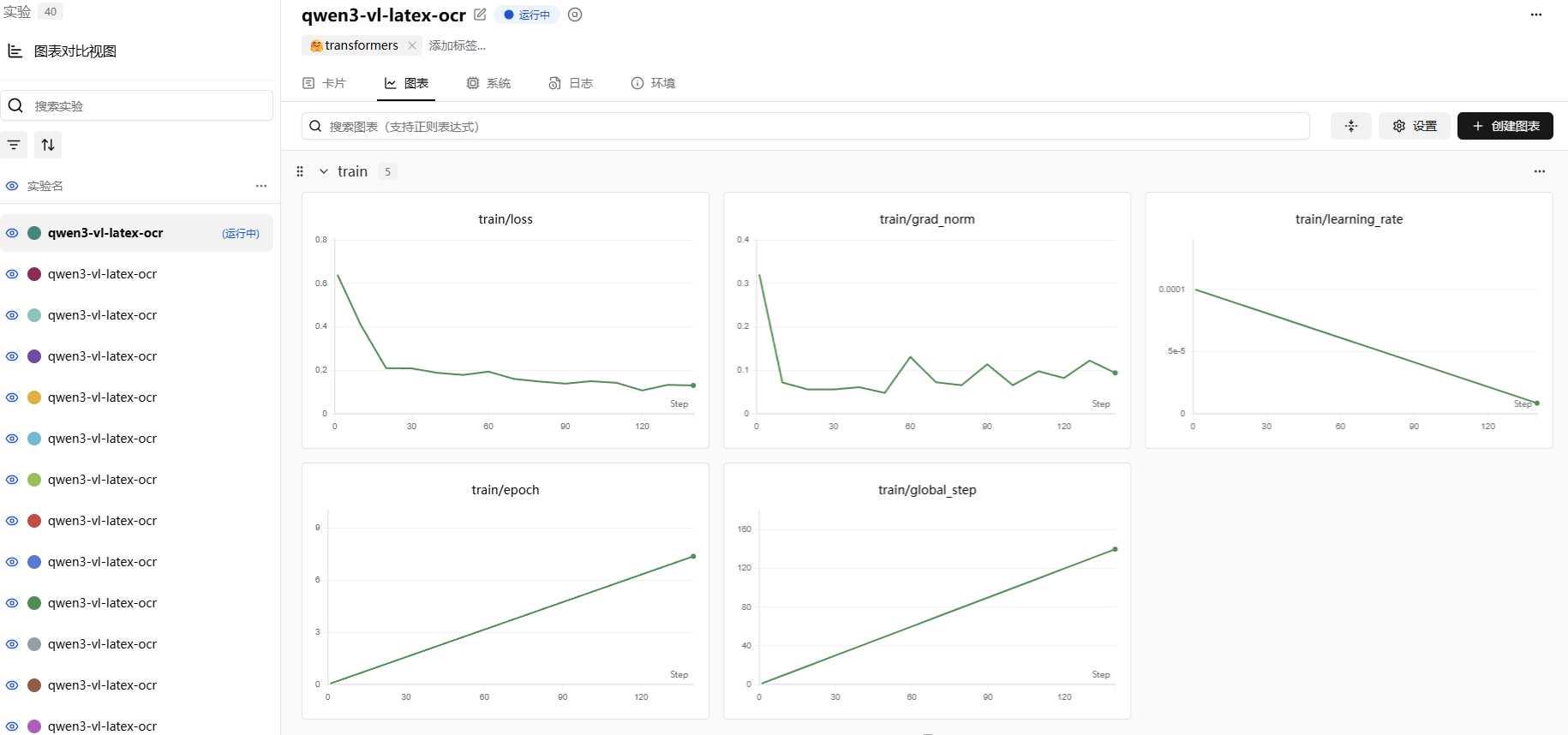
从图的效果看,loss基本都处于一个稳定下降的状态,证明我们的训练效果是在拟合数据集的。
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct
下面的图是Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型微调图表,batch size为1。
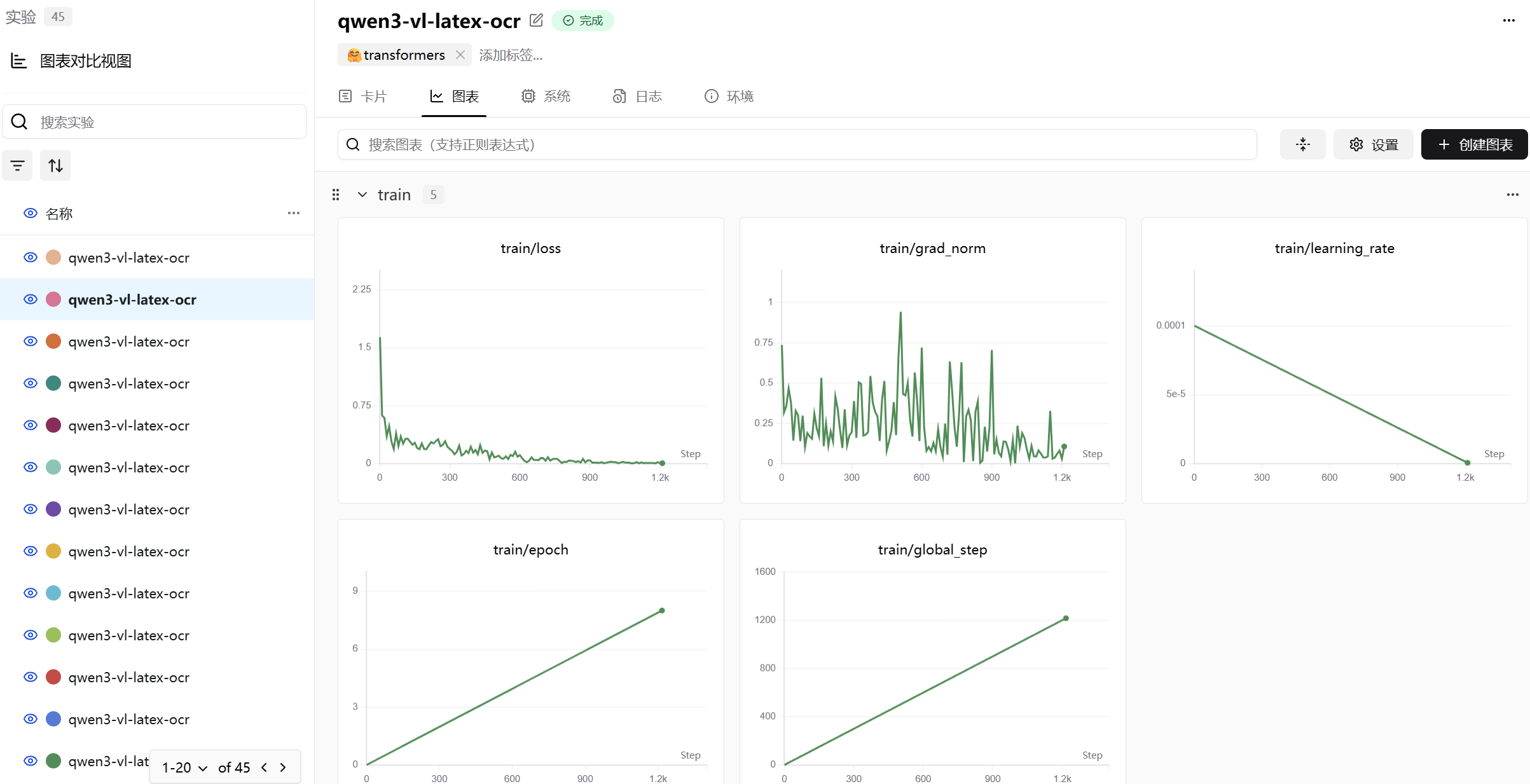
下面的图是qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct模型微调图表,batch size为8。
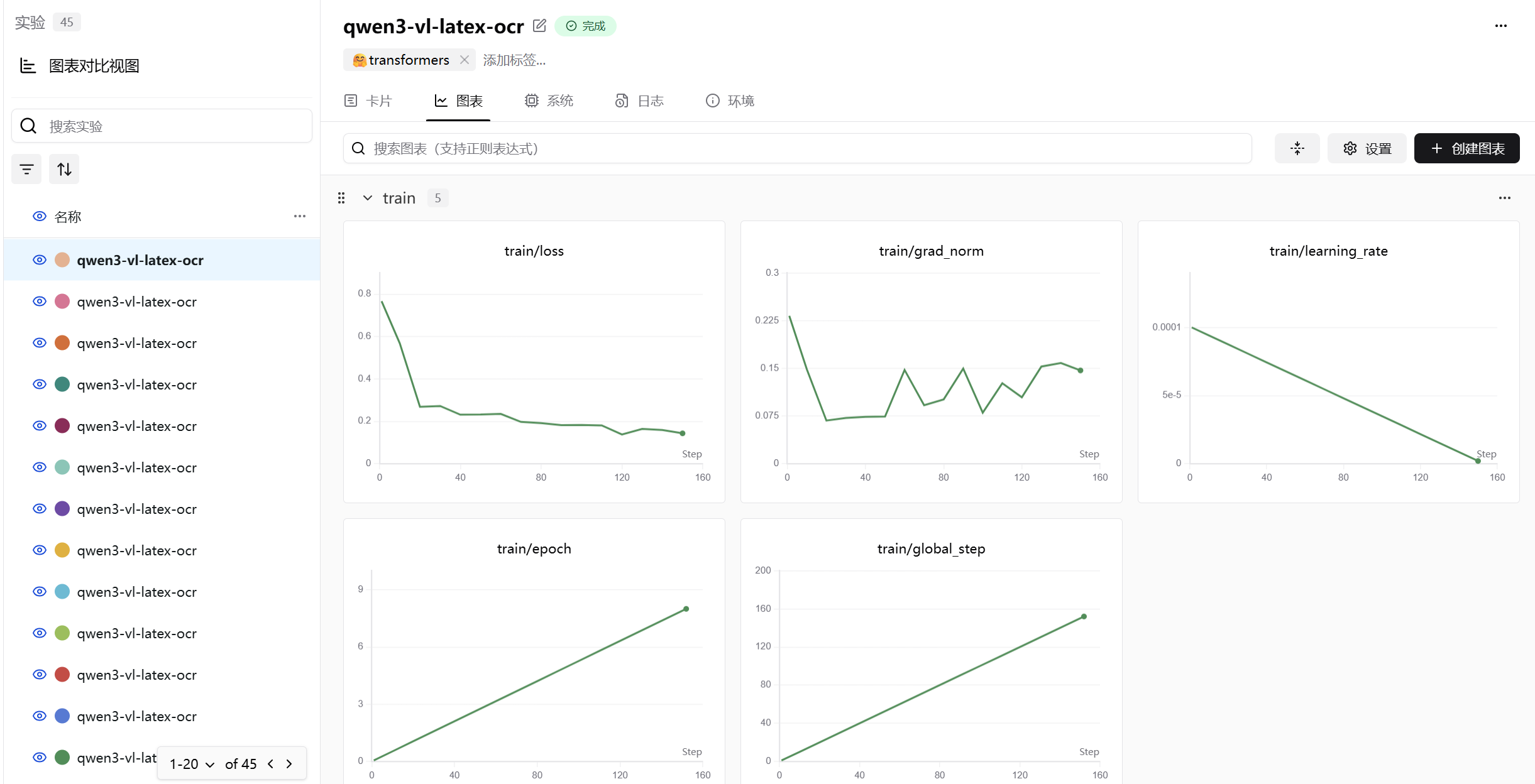
微调后模型效果展示
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct
微调前后模型效果对比1。
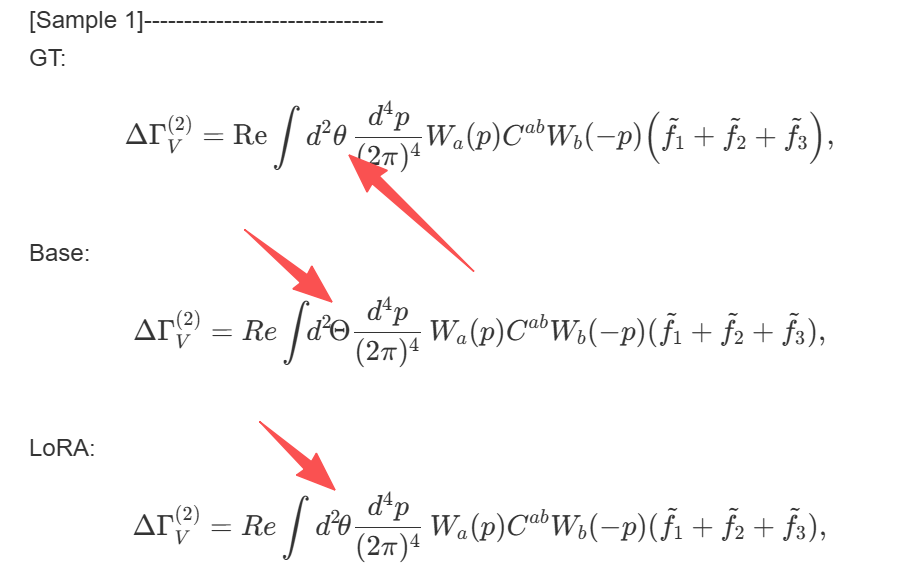
微调前后模型效果对比2。
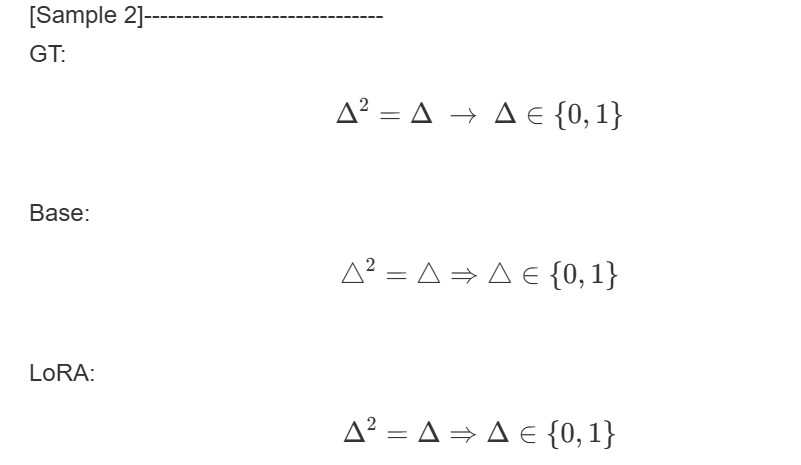 微调前后模型效果对比3。
微调前后模型效果对比3。
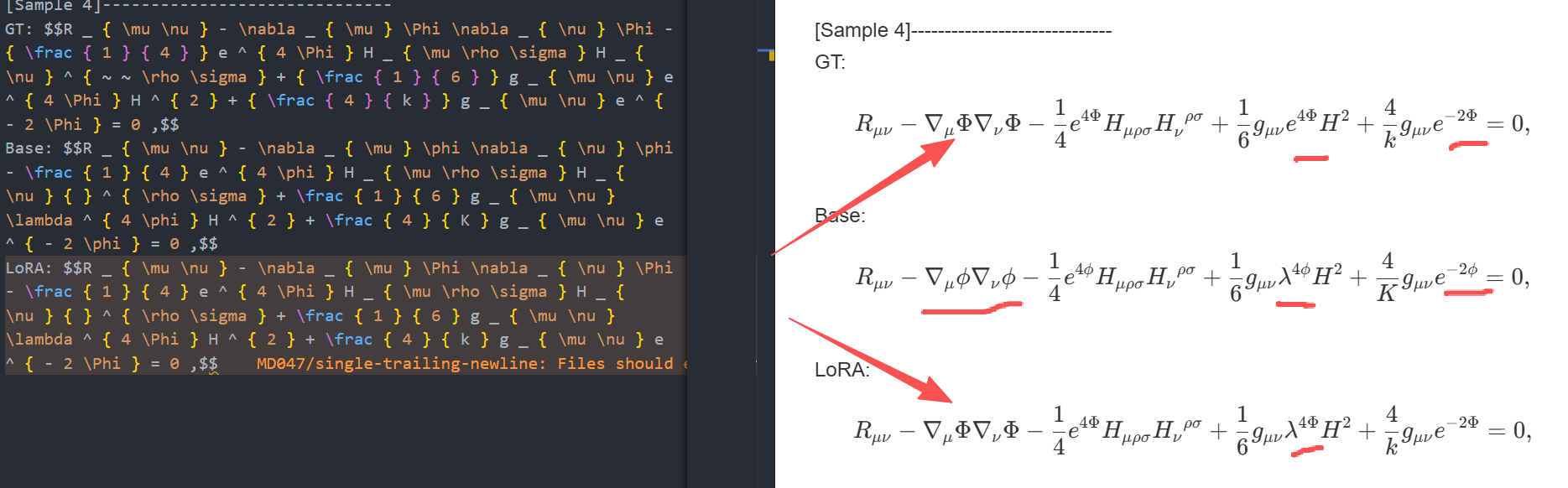
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct
微调前后模型效果对比1,这里是使用batch size为1,训练出来的效果,可以看到这里是较差的提取效果。 
微调前后模型效果对比2,这里是使用batch size为8,训练出来的效果,可以看到效果比之前好很多。 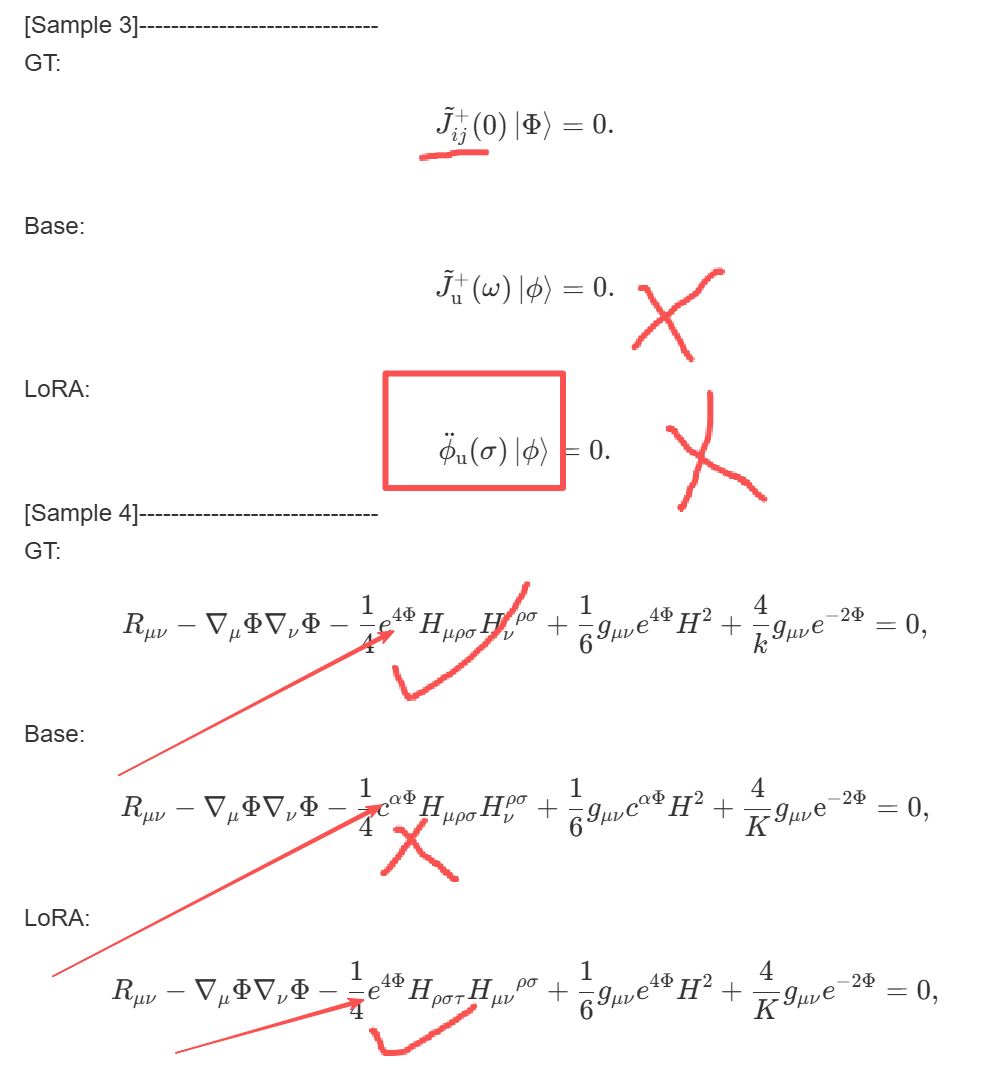
总结
上面显示的是微调前后模型效果对比。
虽然看似 Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct 部分示例里面前后对比是有提升的,不过我也发现模型在微调之后出现了其他的问题。
比如偶尔有一些示例不如微调前的模型,我觉得是模型有点过拟合导致的。因为从微调的图表中就显示了,我们训练的轮次有些过于多了。
本次模型微调里面我也不仅仅微调了一次,而是多次。
刚开始我只是设置了一轮的微调,但是效果并不好,微调前后模型输出的内容几乎一模一样,两轮也是类似的。
接着我慢慢调整训练轮次,在轮次到9的时候,很明显loss不再是一直向下,反倒是有部分上升了,我觉得就先设置训练轮次为8了。
本来我是想要使用手写公式识别的数据集进行训练的。
不过训练的过程中,模型拟合似乎并不好,因为手写的公式数据集里面,不同的一个字符写法可能有很多种,如果我在仅仅使用少量数据集的情况下进行训练,模型微调的效果并不好,于是,换回了非手写的公式。
还有一点是 batch size 的设置,这个参数对训练结果有较大的影响,从 Qwen/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct 能看出来, batch size 设置为1的时候,模型训练的效果会差一些,我估计是过拟合了,batch size 设置为8的时候,效果相比来说比较好。
感兴趣的读者,可以试试其他的参数设置,比如rank,lora_alpha、学习率,batch_size等等,然后对比前后调整的差异。
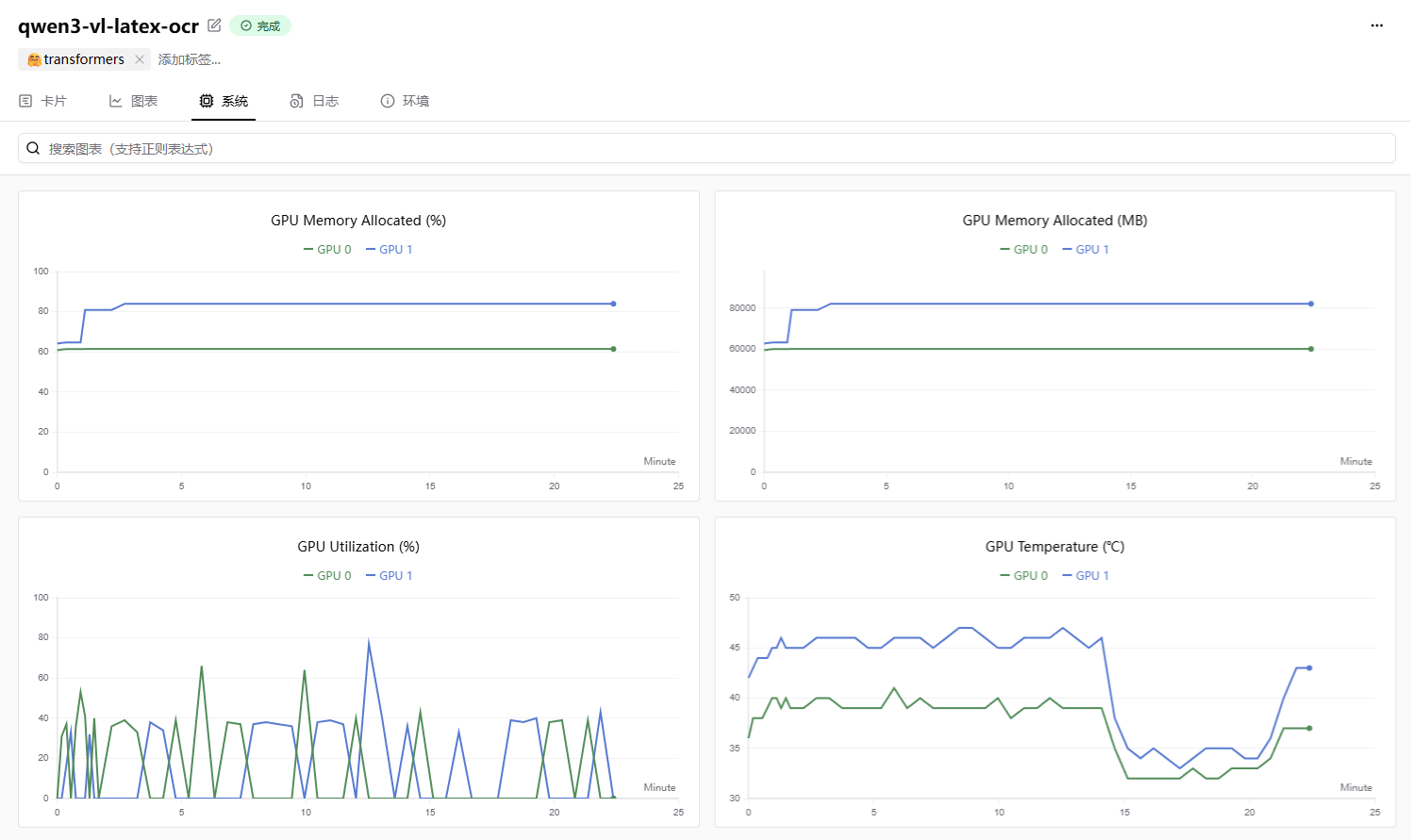
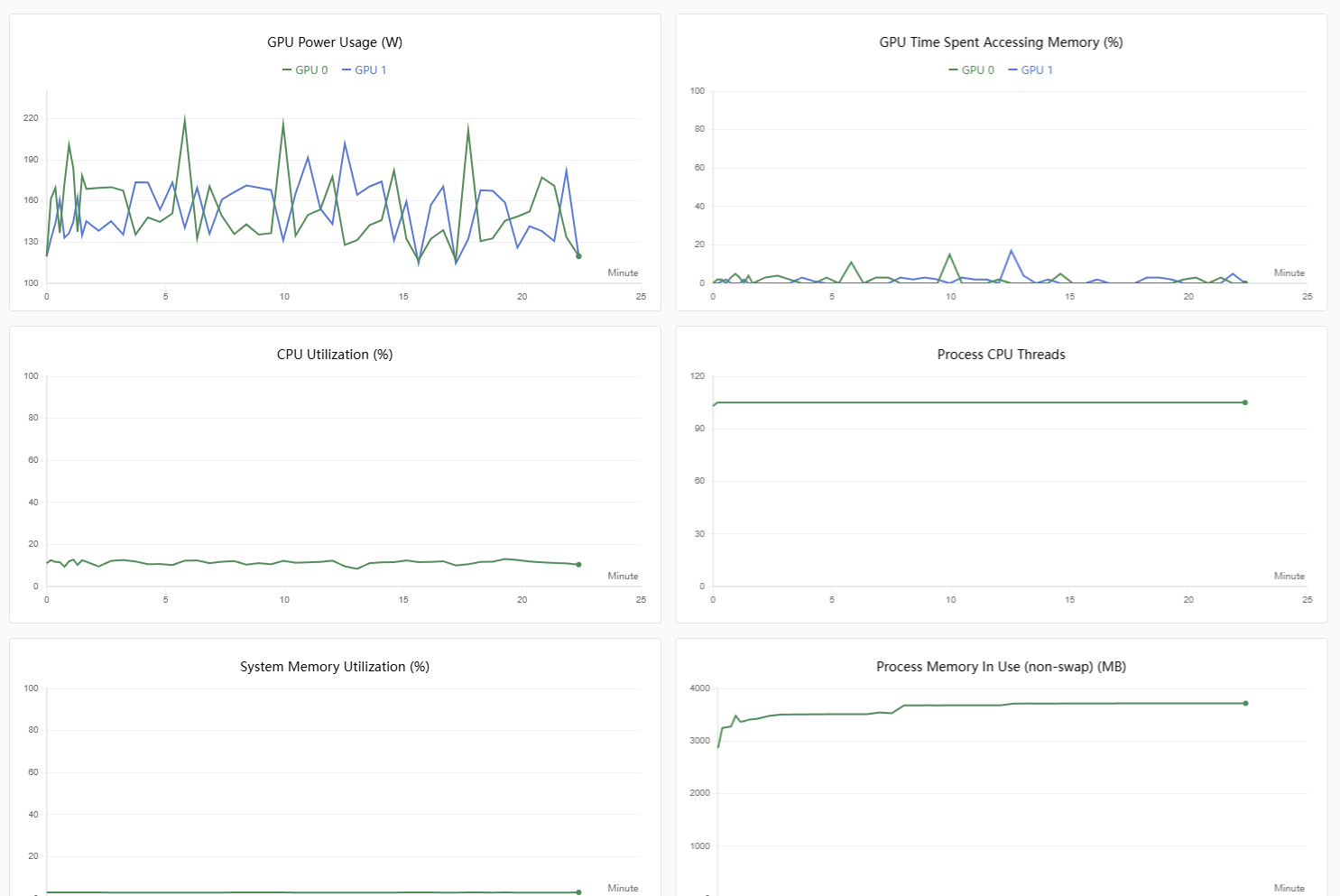
补充模型训练信息
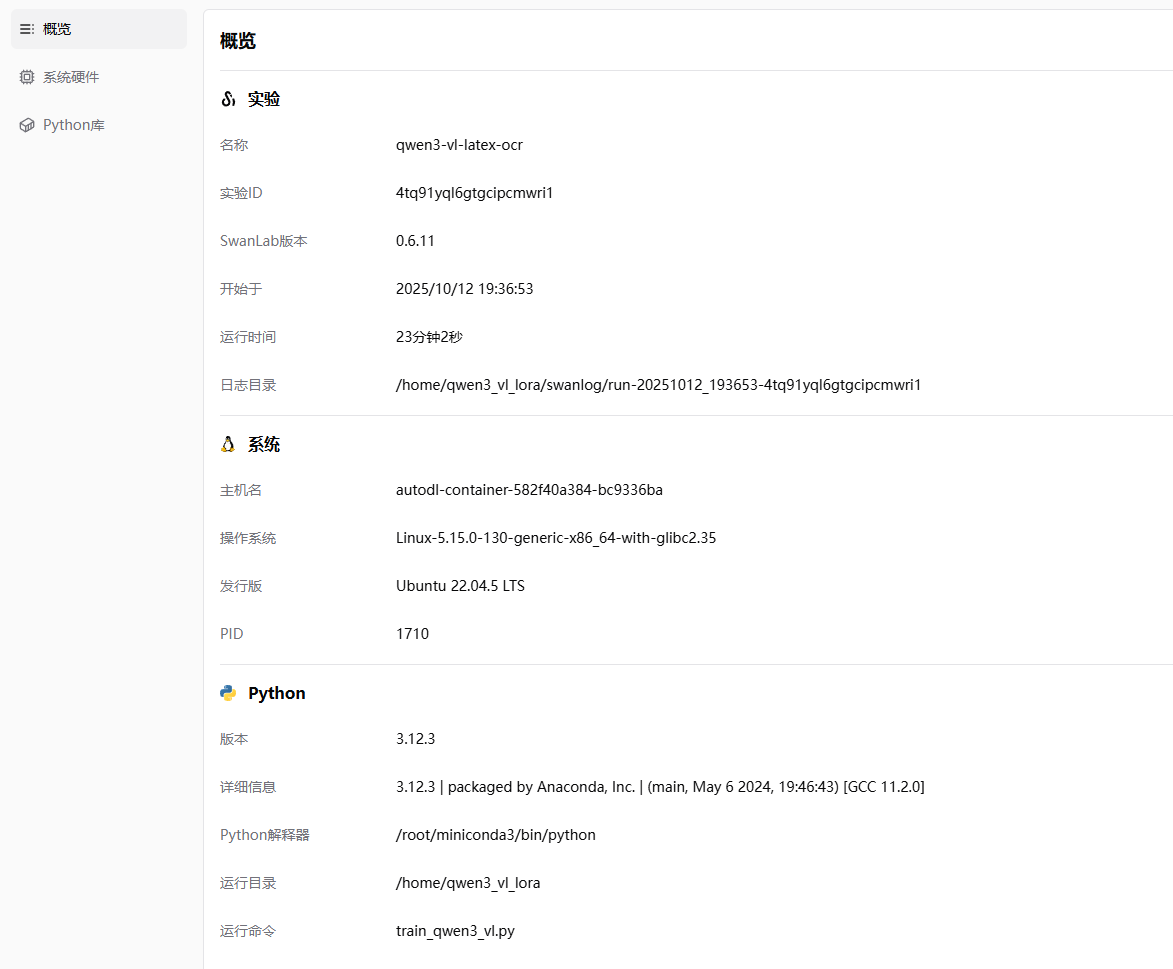
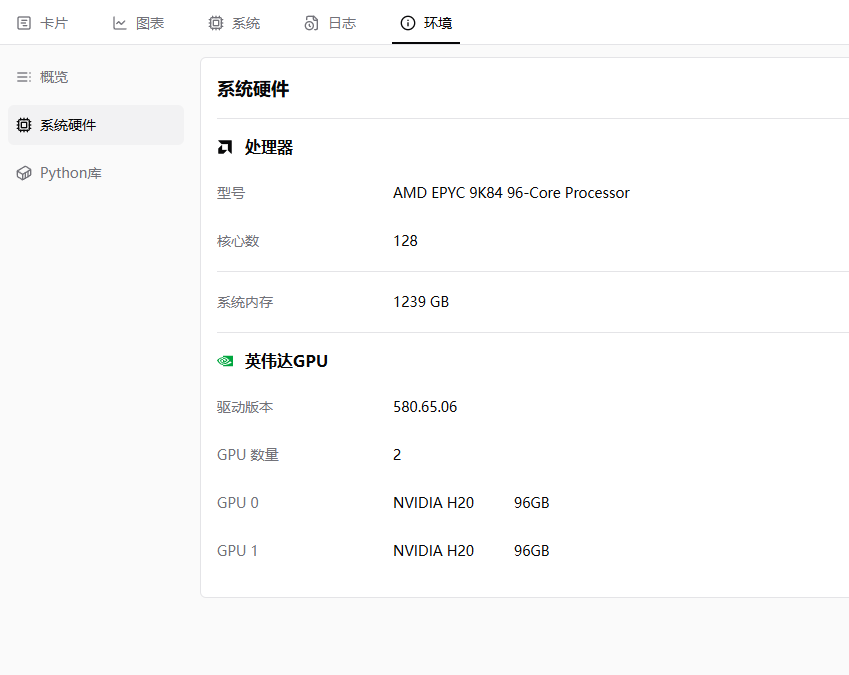
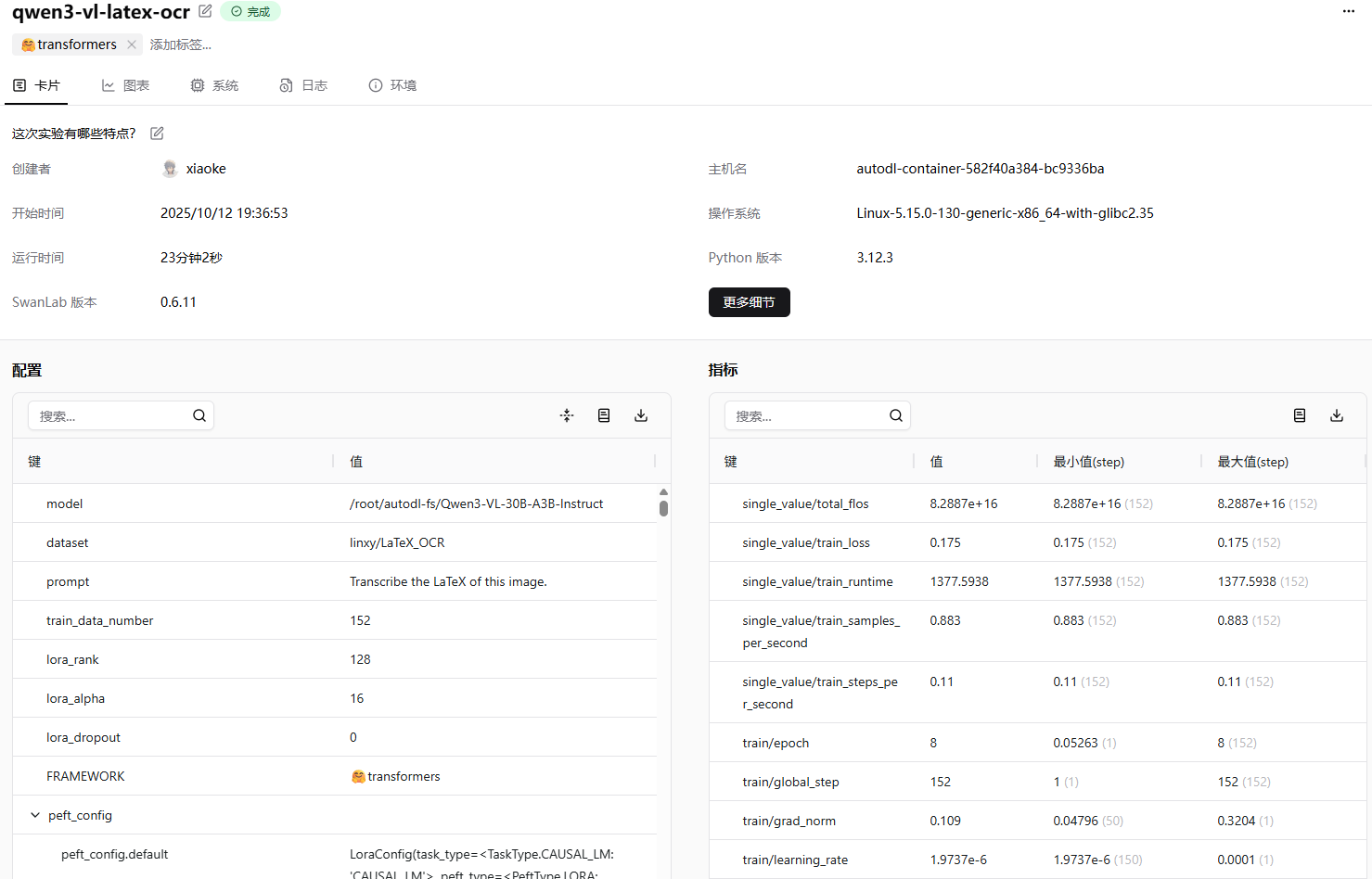
常见错误解决办法
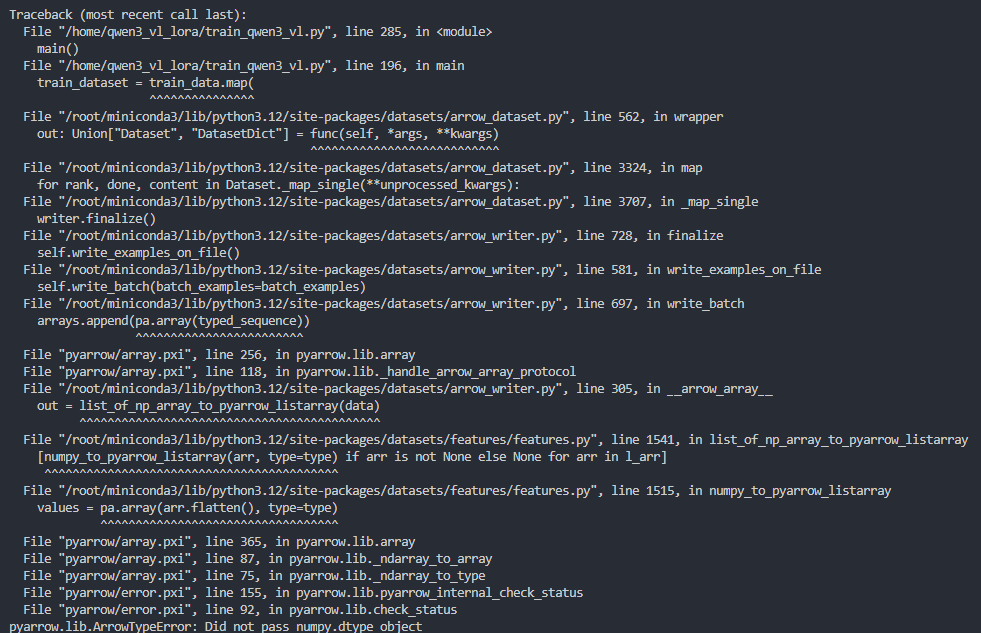 如果遇到上图所示的错误,也就是:
如果遇到上图所示的错误,也就是:
pyarrow.lib.ArrowTypeError: Did not pass numpy.dtype object这种情况,我觉得是由于numpy的版本导致的。 你可以使用下面的命令进行版本修复:
pip install --upgrade numpy运行这个命令,然后重新运行代码, 应该是可以修复这个错误的。
